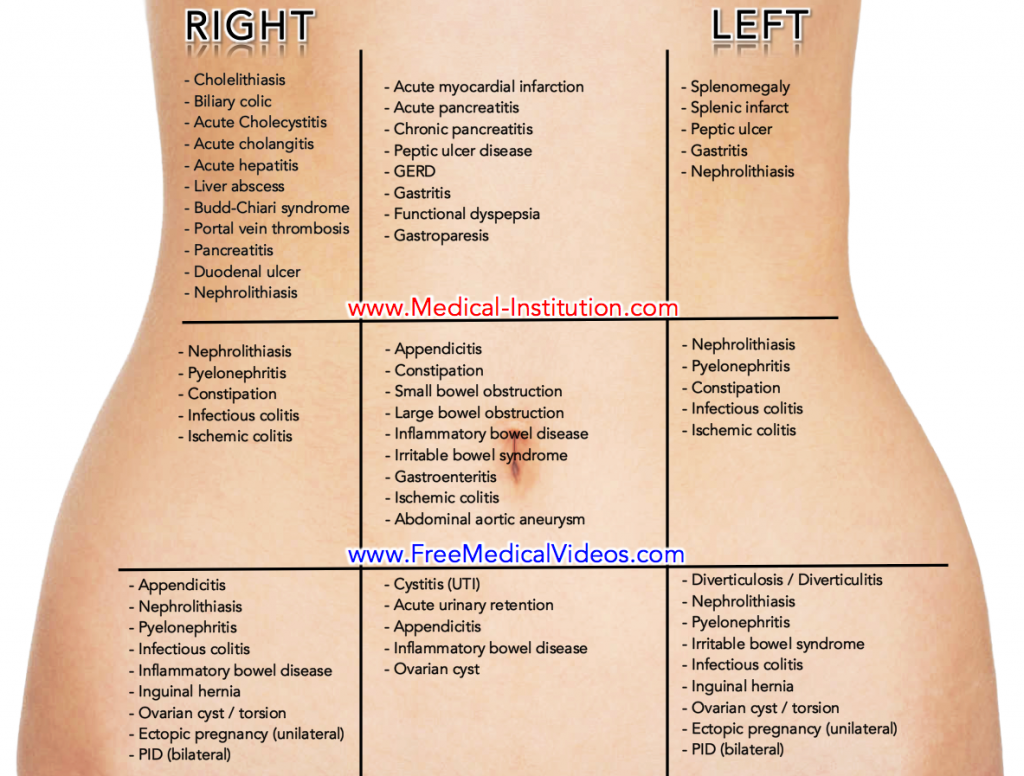
Abdominal Pain Differential Diagnosis Based On Location When possible, the history should be obtained from a nonsedated patient. 7 the initial differential diagnosis can be determined by a delineation of the pain's location, radiation, and movement (e. Differential diagnoses for epigastric pain. pain and tenderness in the epigastrium may be associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd) and gastritis. these often present with heartburn, regurgitation, coughing, and even chest pain. gastric ulcers can also cause pain in the epigastric region.

Acute Abdominal Pain Differential Diagnosis And Initial Pain Generally, suggesting a rational differential diagnosis and planning a suitable diagnostic and management approach have always been challenging for primary care physicians when treating patients with abdominal pain. one challenging aspect of abdominal pain treatment is the request for appropriate paraclinical diagnostic tests . in fact. Abdominal pain is a common problem. most patients have a benign and or self limited etiology, and the initial goal of evaluation is to identify those patients with a serious etiology that may require urgent intervention. a history and focused physical examination will lead to a differential diagnosis of abdominal pain, which will then inform. Elf limited disease to surgical emergencies. evaluating abdominal pain requires an approach that relies on the likelihood of disease, patient history, physical examina. ion, laboratory tests, and. Abdominal pain is common and often inconsequential. acute and severe abdominal pain, however, is almost always a symptom of intra abdominal disease. it may be the sole indicator of the need for surgery and must be attended to swiftly: gangrene and perforation of the gut can occur < 6 hours from onset of symptoms in certain conditions (eg.

Differential Diagnosis Abdominal Pain Left Lower Quadrant At Christine Elf limited disease to surgical emergencies. evaluating abdominal pain requires an approach that relies on the likelihood of disease, patient history, physical examina. ion, laboratory tests, and. Abdominal pain is common and often inconsequential. acute and severe abdominal pain, however, is almost always a symptom of intra abdominal disease. it may be the sole indicator of the need for surgery and must be attended to swiftly: gangrene and perforation of the gut can occur < 6 hours from onset of symptoms in certain conditions (eg. Therefore, the differential diagnosis of abdominal pain can be organized based on whether patients are presenting with their first episode of acute abdominal pain, a recurrent episode of acute abdominal pain, or chronic subacute abdominal pain. table 3 1 outlines the typical time course associated with different diseases causing abdominal pain. Introduction. abdominal pain is one of the most common complaints of patients admitted to emergency units, accounting for 5% – 10% of all presentations. 1,2,3 evaluation of the emergency department patient with acute abdominal pain may be difficult as several factors can obscure the clinical findings resulting in incorrect diagnoses and subsequent adverse outcomes. 4 primary care.
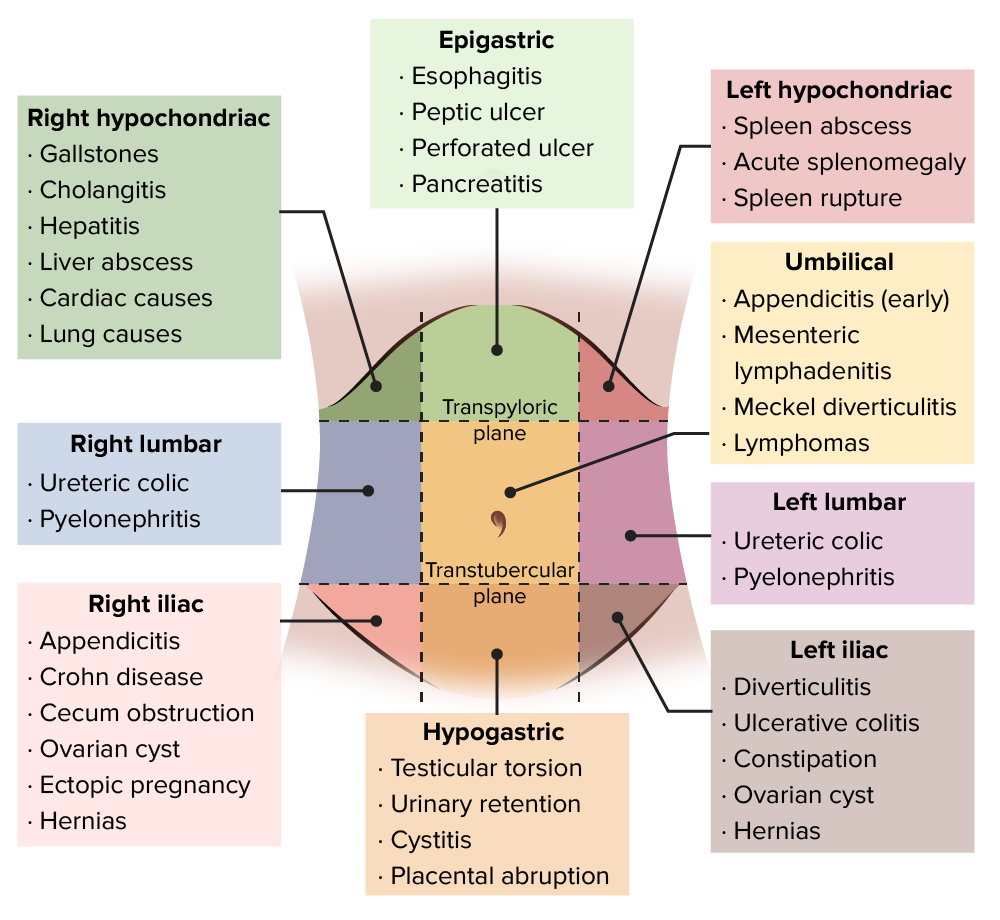
Differential Diagnosis Abdominal Pain Right Lower Quadrant At Samuel Therefore, the differential diagnosis of abdominal pain can be organized based on whether patients are presenting with their first episode of acute abdominal pain, a recurrent episode of acute abdominal pain, or chronic subacute abdominal pain. table 3 1 outlines the typical time course associated with different diseases causing abdominal pain. Introduction. abdominal pain is one of the most common complaints of patients admitted to emergency units, accounting for 5% – 10% of all presentations. 1,2,3 evaluation of the emergency department patient with acute abdominal pain may be difficult as several factors can obscure the clinical findings resulting in incorrect diagnoses and subsequent adverse outcomes. 4 primary care.

Comments are closed.