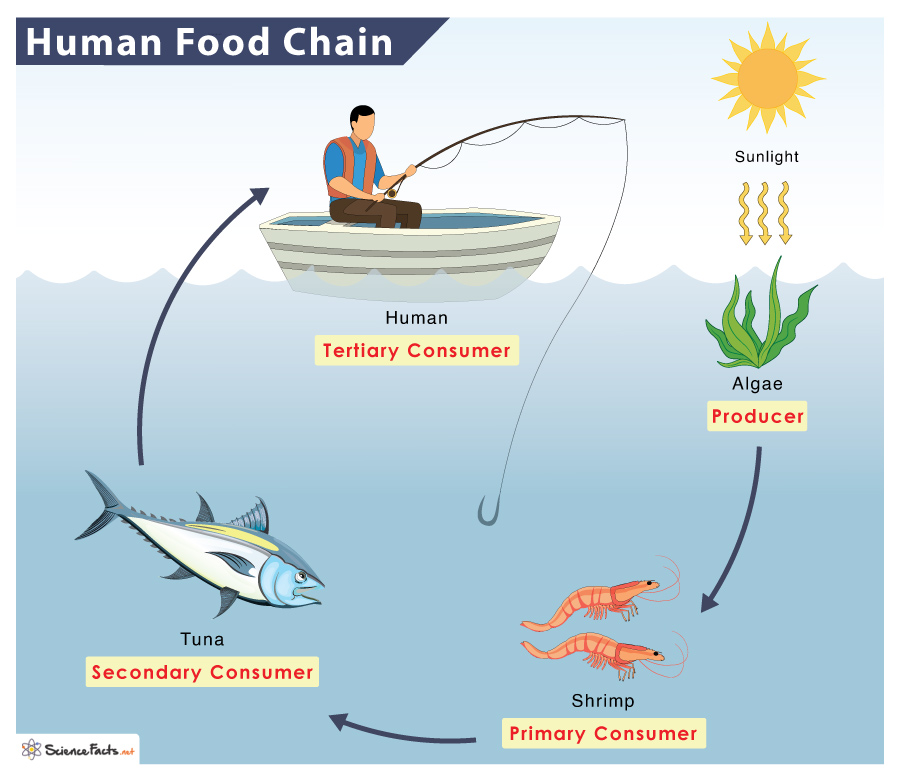
Food Chain Of A Human Examples And Diagram Secondary consumer definition. secondary consumers are organisms that eat primary consumers for energy. primary consumers are always herbivores, or organisms that only eat autotrophic plants. however, secondary consumers can either be carnivores or omnivores. carnivores only eat other animals, and omnivores eat both plant and animal matter. A typical human food chain is three or four organisms long. plants, or algae being the producer, are at the bottom of the food chain. herbivores like cows, goats, pigs, and sheep, the primary consumer of the food chain, follow them. when humans feed on the primary consumers, they become secondary or apex consumers in this food chain.
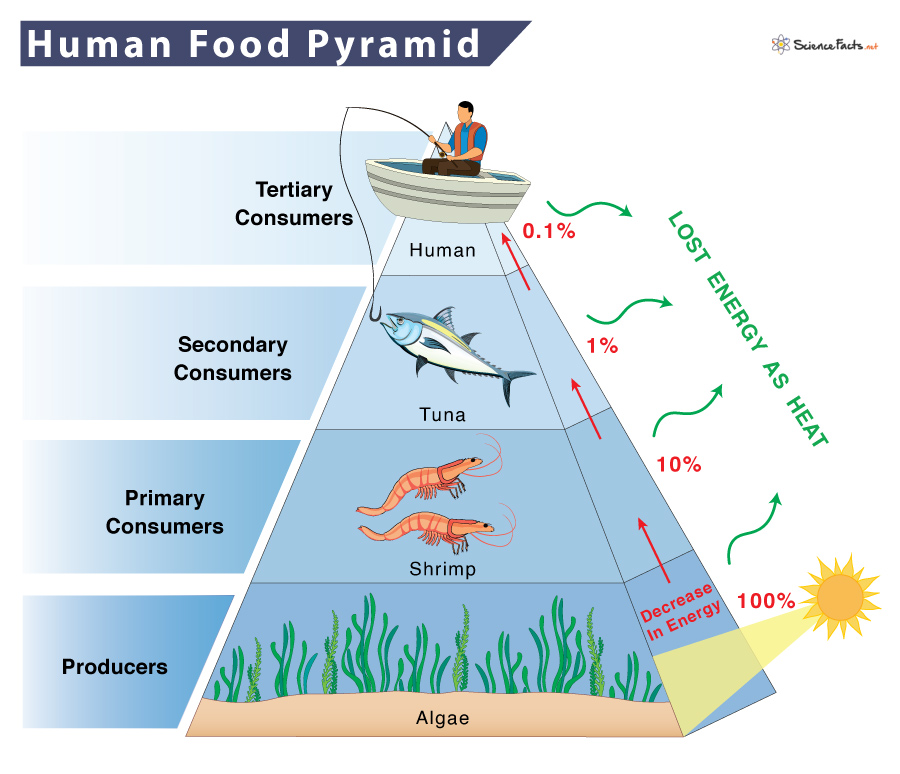
Food Chain Of A Human Examples And Diagram This is also the amount of energy per year that's made available to the primary consumers, which eat the primary producers. the 10 % rule would predict that the primary consumers store only 2, 000 kcal m 2 year of energy in their own bodies, making energy available to their predators (secondary consumers) at a lower rate. 3rd trophic level: secondary consumer. consumes primary consumers. snakes eat mice. 4th trophic level: tertiary consumer. consumes secondary consumers. hawks eat snakes. many consumers feed at more than one trophic level. humans, for example, are primary consumers when they eat plants such as vegetables. These are called primary consumers, or herbivores. deer, turtles, and many types of birds are herbivores. secondary consumers eat the herbivores. tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. there may be more levels of consumers before a chain finally reaches its top predator. top predators, also called apex predators, eat other consumers. Within an ecological food chain, consumers are categorized into primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers. [3] primary consumers are herbivores, feeding on plants or algae. caterpillars, insects, grasshoppers, termites and hummingbirds are all examples of primary consumers because they only eat autotrophs (plants).

Secondary Consumers Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript These are called primary consumers, or herbivores. deer, turtles, and many types of birds are herbivores. secondary consumers eat the herbivores. tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. there may be more levels of consumers before a chain finally reaches its top predator. top predators, also called apex predators, eat other consumers. Within an ecological food chain, consumers are categorized into primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers. [3] primary consumers are herbivores, feeding on plants or algae. caterpillars, insects, grasshoppers, termites and hummingbirds are all examples of primary consumers because they only eat autotrophs (plants). Secondary consumers nearly always consume both producers and primary consumers and are therefore usually classed as omnivores. secondary consumers make up the third trophic level of the food chain and are – as are all consumers – heterotrophs. tertiary consumers. examples of tertiary consumers are hawks, snakes, crocodiles and some big cats. The organisms that consume the producers are herbivores: the primary consumers. secondary consumers are usually carnivores that eat the primary consumers. tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the.
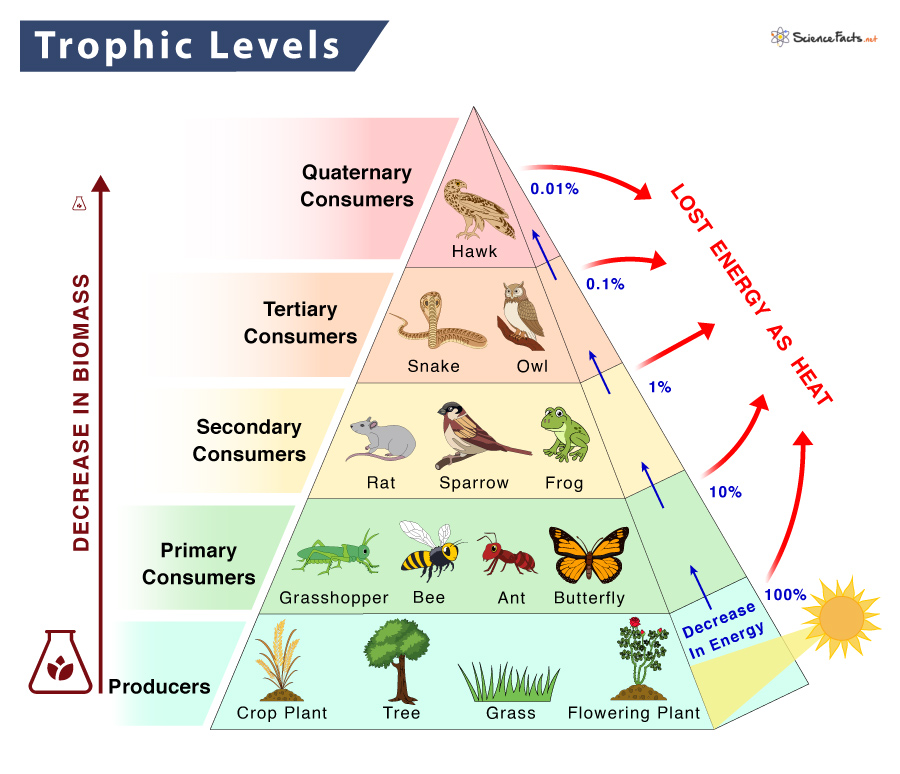
Trophic Level Pyramid Secondary consumers nearly always consume both producers and primary consumers and are therefore usually classed as omnivores. secondary consumers make up the third trophic level of the food chain and are – as are all consumers – heterotrophs. tertiary consumers. examples of tertiary consumers are hawks, snakes, crocodiles and some big cats. The organisms that consume the producers are herbivores: the primary consumers. secondary consumers are usually carnivores that eat the primary consumers. tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the.
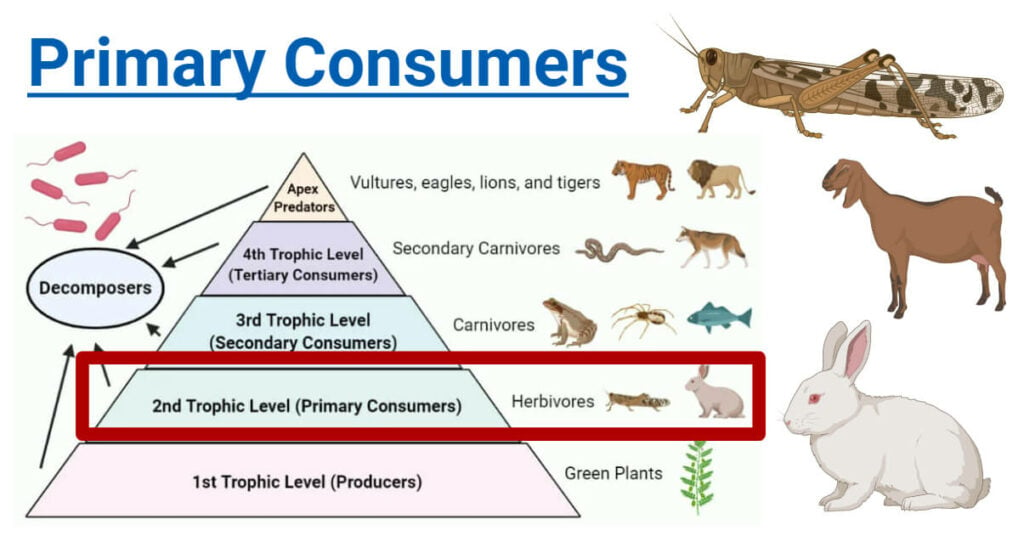
Primary Consumers Definition Food Chain Examples Roles

Comments are closed.