
Botanist Backyard Evolution Of Plants This all happened 345 million years ago. it was another 120 million years until the next big change occurred the arrival of the first true seed bearing plants. this was 225 million years ago, and they are the relatives of our conifers (pine trees etc) and cycads sometimes called cone bearing plants. this period lasted some 90 million years. Sabrina sewell, botanist explore the biology of plants in this introduction to general plant anatomy, morphology, physiology, evolution and development. this course presents the fundamental information about plants upon which learn more. sat 9. saturday, november 9 | 1:00 pm 3:00 pm basic botany: fundamentals of plant biology.
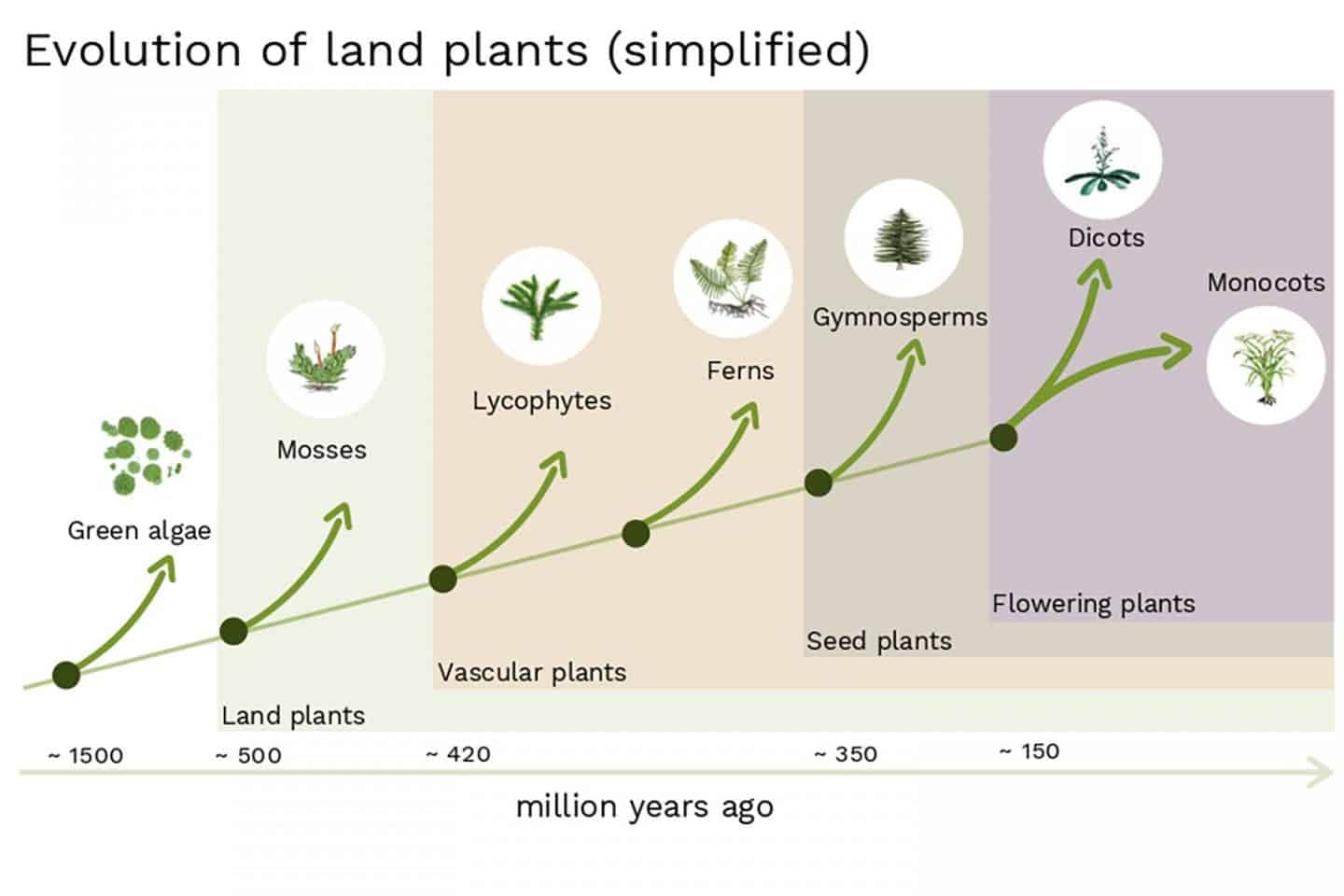
Evolution Of Land Plants Diagram Land plants evolved from a group of freshwater green algae, perhaps as early as 850 mya, [3] but algae like plants might have evolved as early as 1 billion years ago. [2] the closest living relatives of land plants are the charophytes, specifically charales; if modern charales are similar to the distant ancestors they share with land plants, this means that the land plants evolved from a. The exhibition came to the huntington from the new york botanical garden, where it was organized by darwin expert david kohn, professor emeritus of science and society at drew university. “kohn amply illustrates that darwin’s early work in botany was the basis for his theories of evolution,” says david zeidberg, the avery director of the. Botany is the scientific study of plants and plant like organisms. it helps us understand why plants are so vitally important to the world. plants start the majority of food and energy chains, they provide us with oxygen, food and medicine. plants can be divided into two groups: plants 1 1 and plants 2 2. plants 1 1 contain all photosynthetic. Plant evolution, paleobotany, photosynthesis: at present, fossil evidence of land plants dates to the ordovician period. the abundance and diversity of plant fossils increase into the silurian period, and by the middle devonian period, the heterosporous life cycle, which allows for more rapid evolution, had occurred independently in several groups, including lycophytes and the ancestors of.
How Plants Evolved To Follow Gravity Botany is the scientific study of plants and plant like organisms. it helps us understand why plants are so vitally important to the world. plants start the majority of food and energy chains, they provide us with oxygen, food and medicine. plants can be divided into two groups: plants 1 1 and plants 2 2. plants 1 1 contain all photosynthetic. Plant evolution, paleobotany, photosynthesis: at present, fossil evidence of land plants dates to the ordovician period. the abundance and diversity of plant fossils increase into the silurian period, and by the middle devonian period, the heterosporous life cycle, which allows for more rapid evolution, had occurred independently in several groups, including lycophytes and the ancestors of. The mission of the department of systematic and evolutionary botany with its collections (the new and old botanic gardens, herbarium) and the associated university library plant sciences ) is to: increase knowledge about plant diversity, the processes and patterns of plant evolution, the relationships between plants and other organisms and. The future of plant mating system studies in the era of next generation sequencing. a generation ago research on plant mating systems blossomed with the widespread availability of co dominant genetic markers (brown and allard, 1970), facilitating studies of outcrossing rates and patterns of paternity.

Evolution Of Land Plants Diagram The mission of the department of systematic and evolutionary botany with its collections (the new and old botanic gardens, herbarium) and the associated university library plant sciences ) is to: increase knowledge about plant diversity, the processes and patterns of plant evolution, the relationships between plants and other organisms and. The future of plant mating system studies in the era of next generation sequencing. a generation ago research on plant mating systems blossomed with the widespread availability of co dominant genetic markers (brown and allard, 1970), facilitating studies of outcrossing rates and patterns of paternity.

Comments are closed.