
When Quadratic Equation Has No Real Roots Discriminant Revisited Quadratic function discriminant should be negative for non real roots.anil kumar: anil.anilkhandelwal@gmail. 1. to show that a polynomial has no real roots, we will try to write it as an equation where the sum of some positive numbers equals a strictly negative number. as the sum of positive numbers cannot be strictly negative, there is a contradiction, which means there's no real root. x8 − x7 x2 − x 15 = 0. subtract 15: x8 − x7 x2 − x.

How Would I Do C If Thereтащs юааnoюаб юааrealюаб юааrootsюаб R 6thform A quadratic equation has real roots when the discriminant is positive or zero (not negative). from an algebra standpoint, this means b2 >= 4ac. visually, this means the graph of the quadratic (a parabola) touches the x axis at least once. of course, a quadratic that touches the x axis only once, at the vertex, has one repeated real root. As a result, the quadratic equation $(1)$ will provide $2$ more real roots matching the result found via the sturm chain. ( credit: oscar lanzi ) for the purposes of this question, the above answer should suffice. The second diagram has one root and the third diagram has no roots. the discriminant can be used in the following way: \({b^2} 4ac\textless0\) there are no real roots (diagram 1). It is important to note that this quadratic inequality is in standard form, with zero on one side of the inequality. step 1: determine the critical numbers. for a quadratic inequality in standard form, the critical numbers are the roots. therefore, set the function equal to zero and solve. − x2 6x 7 = 0.
How Come X Square 1 0 Has No Real Roots The second diagram has one root and the third diagram has no roots. the discriminant can be used in the following way: \({b^2} 4ac\textless0\) there are no real roots (diagram 1). It is important to note that this quadratic inequality is in standard form, with zero on one side of the inequality. step 1: determine the critical numbers. for a quadratic inequality in standard form, the critical numbers are the roots. therefore, set the function equal to zero and solve. − x2 6x 7 = 0. Follow these general steps to ensure that you find every root: use the rational root theorem to list all possible rational roots. pick one root from the list in step 1 and use long division or synthetic division to find out if it is, in fact, a root. if the root doesn’t work, try another guess. if the root works, proceed to step 3. The minimum will be attained at a root of the derivative $4x^3 r$. the only real root is $\sqrt[3]{ r 4}$. thus the condition for no real roots is $(\sqrt[3]{ r 4})^4 r \sqrt[3]{ r 4} s > 0$, and this can still be somewhat simplified.
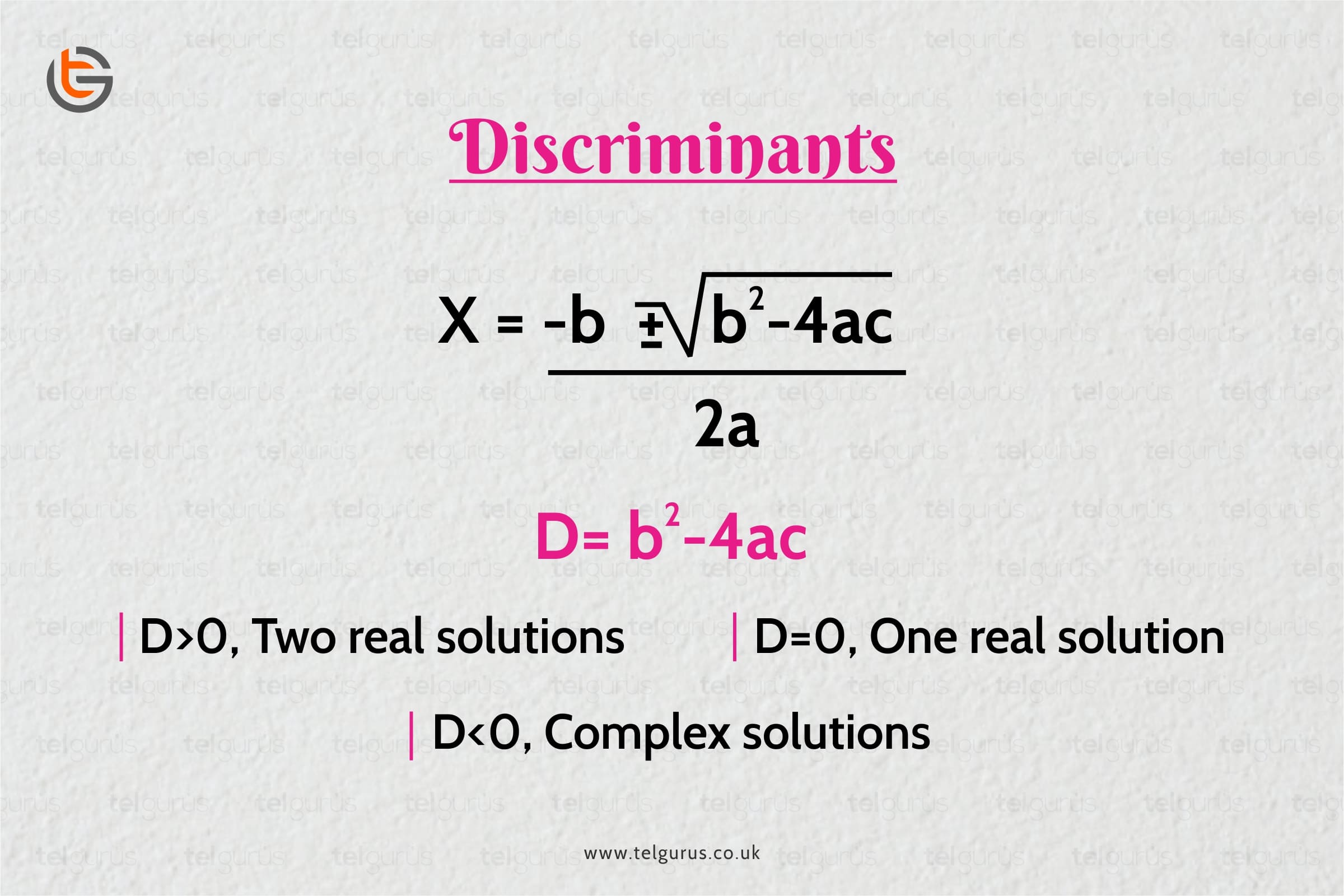
Discriminants And Determining The No Of Real Roots Of A Quadratic Equation Follow these general steps to ensure that you find every root: use the rational root theorem to list all possible rational roots. pick one root from the list in step 1 and use long division or synthetic division to find out if it is, in fact, a root. if the root doesn’t work, try another guess. if the root works, proceed to step 3. The minimum will be attained at a root of the derivative $4x^3 r$. the only real root is $\sqrt[3]{ r 4}$. thus the condition for no real roots is $(\sqrt[3]{ r 4})^4 r \sqrt[3]{ r 4} s > 0$, and this can still be somewhat simplified.

Non Real Roots College Algebra Youtube

Comments are closed.