
Explain How Producers And Consumers Are Different Johnathankruwarmstrong Meaning. producers are those organisms capable of creating their own food in the form of simple sugars by using the elementary components of nature like sunlight, water, co2 etc. consumers are the living organisms that are not capable of synthesising their own food instead they consume the food made by producers. examples. Closest distance to the center is the minor axis or the value of b. Órbita 9 is a spanish colombian science fiction romantic drama movie directed and written by hatem khraiche. directed by hatem khraiche. if you cant beat them orbiter 9 concludes with an odd kind of if you cant beat them join them shrug which seems distinctly in opposition to.

Producers And Consumers Economics Producers are also called autotrophs. auto means self, while troph means food. they are organisms that create their food from inorganic molecules such as water, co2, nitrogen, and phosphate. most. Welcome to producers, consumers, and decomposers with mr. j! need help with what producers, consumers, and decomposers are? you're in the right place!whether. Further trophic levels are numbered subsequently according to how far the organism is along the food chain. level 1: plants and algae make their own food and are called producers. level 2: herbivores eat plants and are called primary consumers. level 3: carnivores that eat herbivores are called secondary consumers. Summary. ecosystems require constant inputs of energy from sunlight or chemicals. producers use energy and inorganic molecules to make food. consumers take in food by eating producers or other living things. decomposers break down dead organisms and other organic wastes and release inorganic molecules back to the environment.
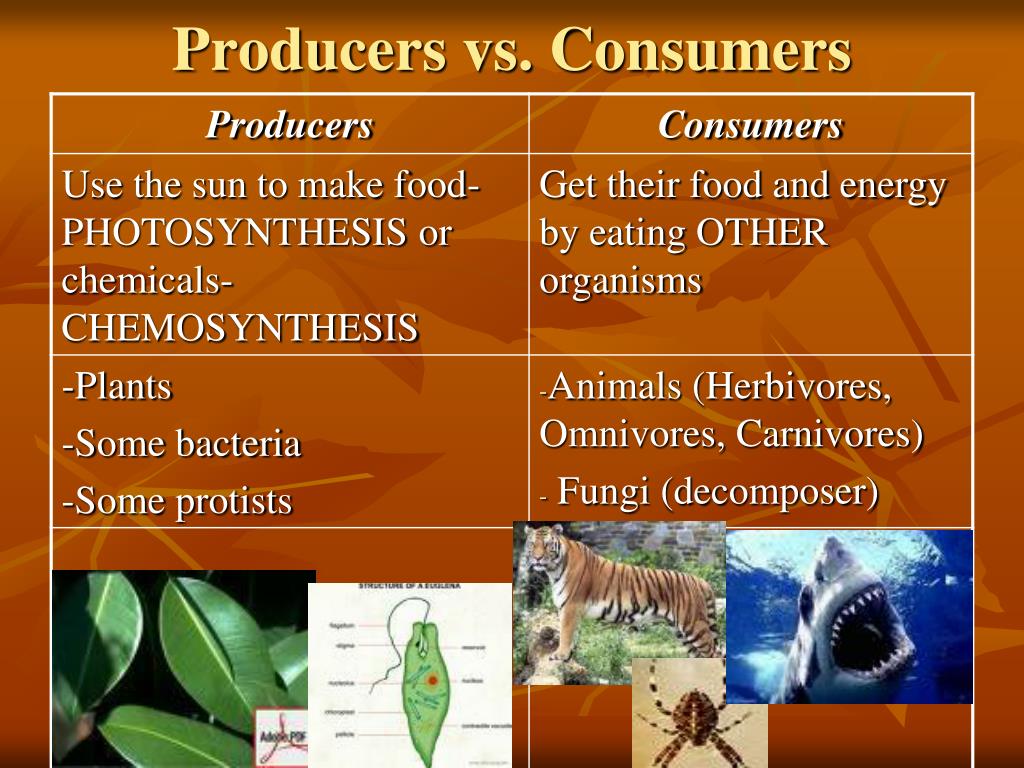
Ppt Interactions Of Life Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id Further trophic levels are numbered subsequently according to how far the organism is along the food chain. level 1: plants and algae make their own food and are called producers. level 2: herbivores eat plants and are called primary consumers. level 3: carnivores that eat herbivores are called secondary consumers. Summary. ecosystems require constant inputs of energy from sunlight or chemicals. producers use energy and inorganic molecules to make food. consumers take in food by eating producers or other living things. decomposers break down dead organisms and other organic wastes and release inorganic molecules back to the environment. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. Here, the producers are consumed by the predators primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. when many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as food web. a food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms. as every organism can feed on multiple things, a food web.

Comments are closed.