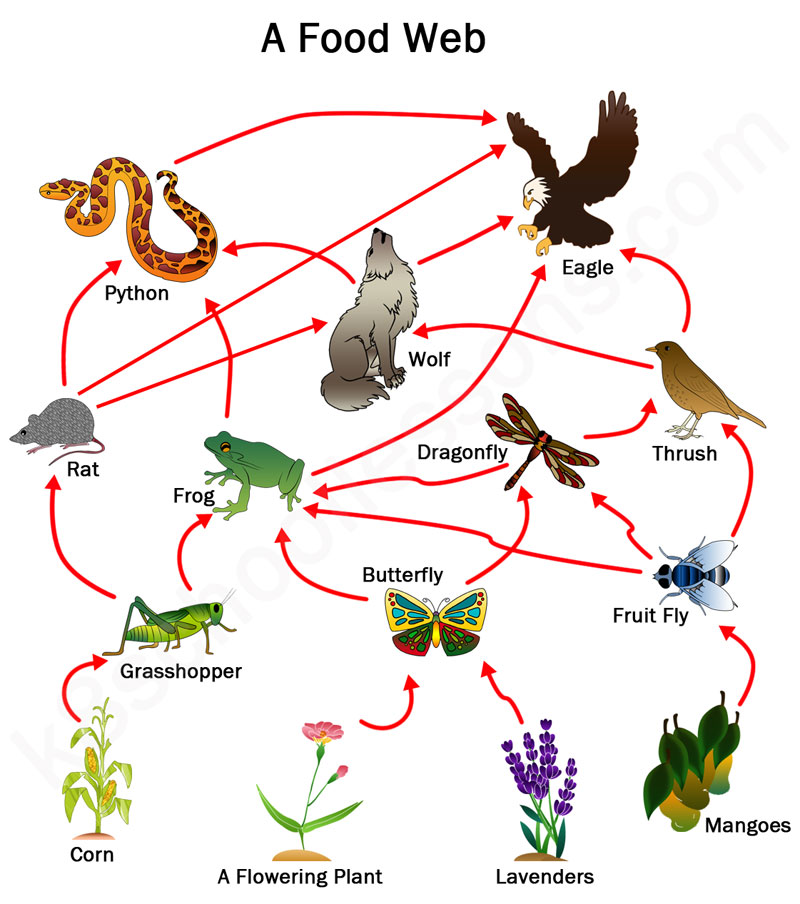
Food Chains And Food Webs Examples Of Food Chains And Food Webs Food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. a food chain shows how matter and energy from food are transferred from one organism to another, whereas a food web illustrates how food chains intertwine in an ecosystem. food webs also demonstrate that most organisms. A food web is a diagram showing an ecosystem's complex feeding relationships. learn about types of food webs and how they differ from a food chain.

Food Chain And Food Webs Explained Scientists often classify food webs based on the type of ecosystem being presented into the following types: 1. connectance food webs. scientists use connectance food webs to depict the predator prey relationship. here, all the arrows on the web are equally weighted. 2. interaction food webs. Vocabulary. a food web consists of all the food chains in a single ecosystem. each living thing in an ecosystem is part of multiple food chains. each food chain is one possible path that energy and nutrients may take as they move through the ecosystem. all of the interconnected and overlapping food chains in an ecosystem make up a food web. The food web is a simplified illustration of the various methods of feeding that link an ecosystem into a unified system of exchange. there are different kinds of consumer–resource interactions that can be roughly divided into herbivory, carnivory, scavenging, and parasitism. Food webs often aggregate many species into trophic groups, which are functional groups of species that have the same predators and prey in a food web. software can be used to model more complex interactions (figure 2), but no food web model can capture all of the complexity found within a natural ecosystem.
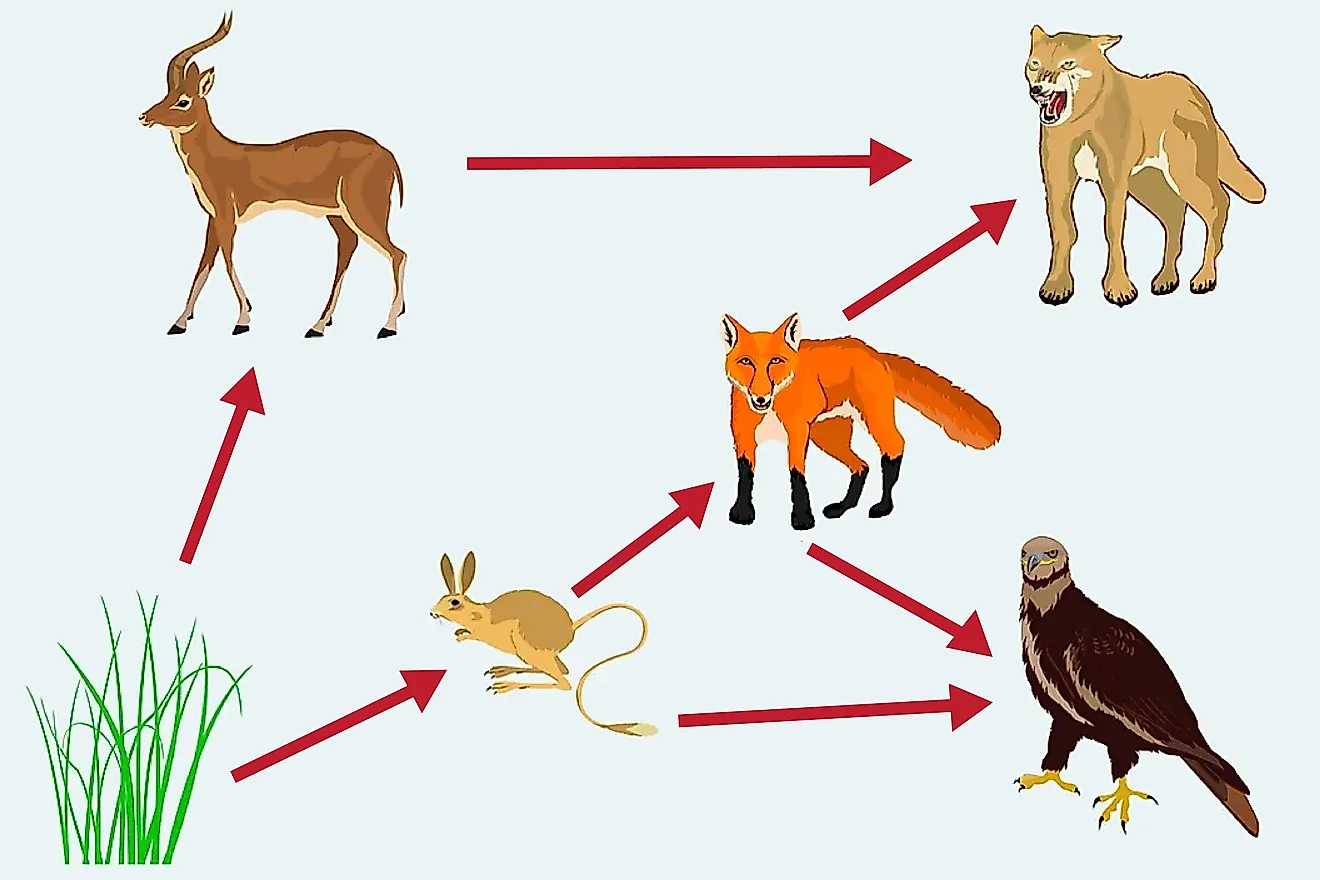
What Is A Food Web Worldatlas The food web is a simplified illustration of the various methods of feeding that link an ecosystem into a unified system of exchange. there are different kinds of consumer–resource interactions that can be roughly divided into herbivory, carnivory, scavenging, and parasitism. Food webs often aggregate many species into trophic groups, which are functional groups of species that have the same predators and prey in a food web. software can be used to model more complex interactions (figure 2), but no food web model can capture all of the complexity found within a natural ecosystem. A food web is a concept that accounts for the multiple trophic interactions between each species (figure \(\pageindex{2}\)). figure \(\pageindex{2}\) this food web shows the interactions between organisms across trophic levels. arrows point from an organism that is consumed to the organism that consumes it. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and.
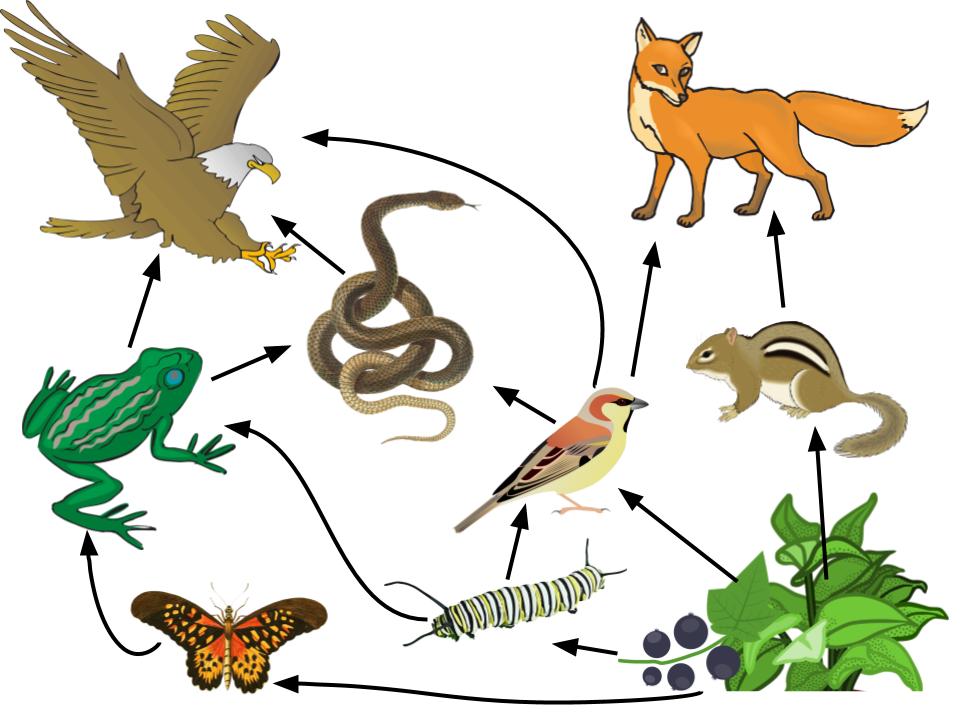
Identify Producer And Consumers On A Food Web A food web is a concept that accounts for the multiple trophic interactions between each species (figure \(\pageindex{2}\)). figure \(\pageindex{2}\) this food web shows the interactions between organisms across trophic levels. arrows point from an organism that is consumed to the organism that consumes it. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and.

Food Webs

Comments are closed.