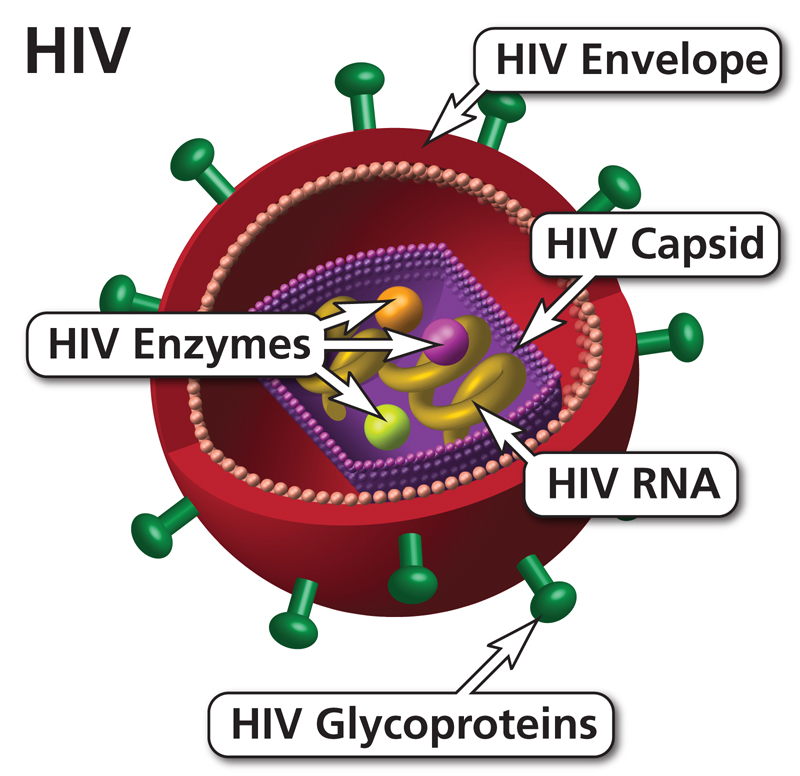
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Hiv Nih Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (aids), is an ongoing, also called chronic, condition. it's caused by the human immunodeficiency virus, also called hiv. hiv damages the immune system so that the body is less able to fight infection and disease. if hiv isn't treated, it can take years before it weakens the immune system enough to become aids. Hiv (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks cells that help the body fight infection, making a person more vulnerable to other infections and diseases. it is spread by contact with certain bodily fluids of a person with hiv, most commonly during unprotected sex (sex without a condom or hiv medicine to prevent or treat hiv), or.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus National Library Of Medicine Pubmed Health Overview. hiv (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks the body's immune system. without treatment, it can lead to aids (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). there is currently no effective cure. once people get hiv, they have it for life. but proper medical care can control the virus. Human immunodeficiency virus (hiv) is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system. acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (aids) occurs at the most advanced stage of infection. hiv targets the body’s white blood cells, weakening the immune system. this makes it easier to get sick with diseases like tuberculosis, infections and some cancers. The human immunodeficiency virus (hiv) is the virus that causes hiv infection. if untreated, hiv may cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (aids) , the most advanced stage of hiv infection. people with hiv who are not on medication and do not have consistent control of their hiv can transmit hiv through vaginal or anal sex, sharing of. Hiv and aids. what is hiv? the human immunodeficiency virus (hiv) targets cells of the immune system, called cd4 cells, which help the body respond to infection. within the cd4 cell, hiv replicates and in turn, damages and destroys the cell. without effective treatment of a combination of antiretroviral (arv) drugs, the immune system will.
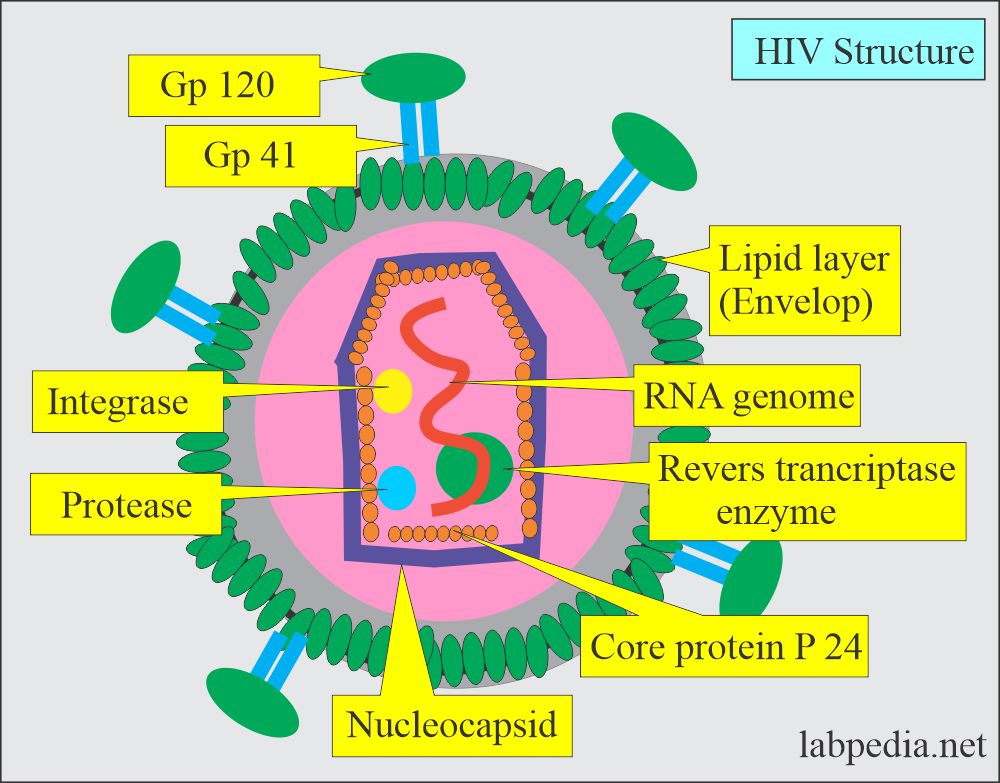
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Hiv Aids Acquired Immunodeficiency The human immunodeficiency virus (hiv) is the virus that causes hiv infection. if untreated, hiv may cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (aids) , the most advanced stage of hiv infection. people with hiv who are not on medication and do not have consistent control of their hiv can transmit hiv through vaginal or anal sex, sharing of. Hiv and aids. what is hiv? the human immunodeficiency virus (hiv) targets cells of the immune system, called cd4 cells, which help the body respond to infection. within the cd4 cell, hiv replicates and in turn, damages and destroys the cell. without effective treatment of a combination of antiretroviral (arv) drugs, the immune system will. The human immunodeficiency virus (hiv) is a type of virus called a retrovirus. it causes aids (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome), which is life threatening. hiv is called an immunodeficiency virus because it weakens (causes deficiency) of your immune system. your immune system helps defend you against infection and cancer. Diagnosis. hiv can be diagnosed through blood or saliva testing. tests include: antigen antibody tests. these tests most often use blood from a vein. antigens are substances on the hiv virus itself. they most often show up in the blood within a few weeks after being exposed to hiv.

Comments are closed.