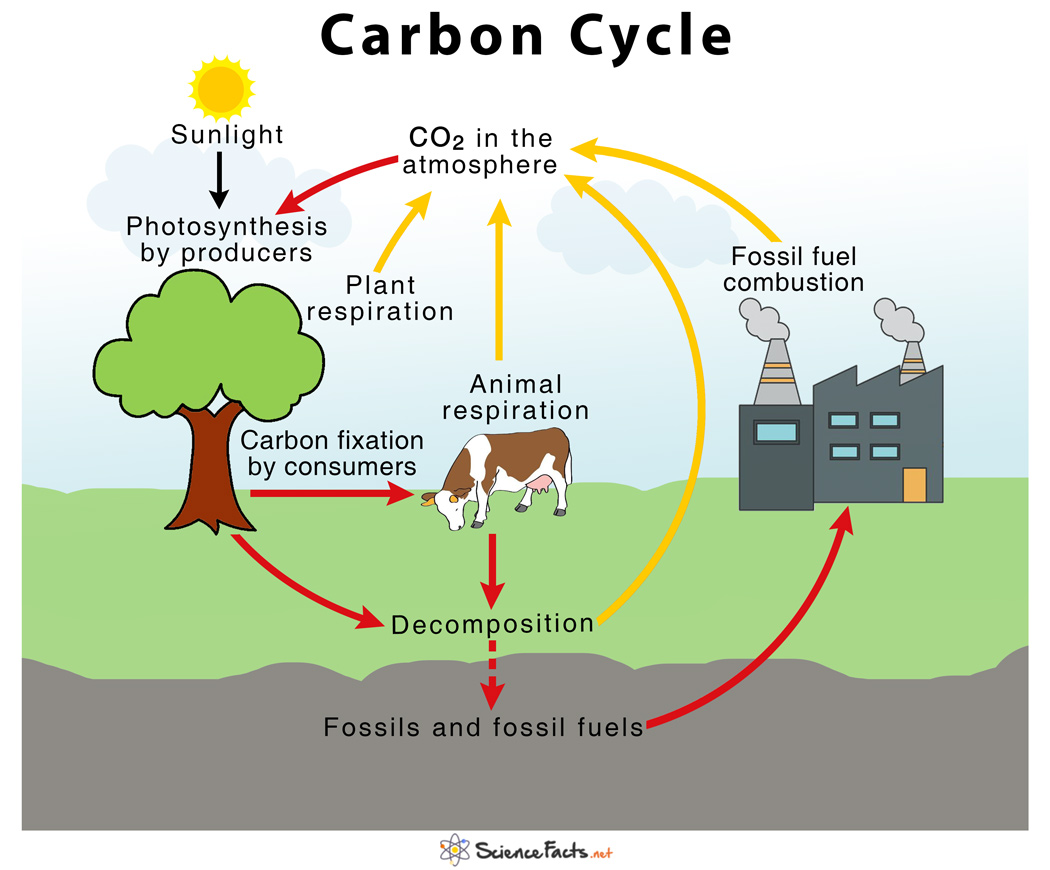
Carbon Cycle With Diagram Atmospheric carbon dioxide comes from two primary sources—natural and human activities. natural sources of carbon dioxide include most animals, which exhale carbon dioxide as a waste product. human activities that lead to carbon dioxide emissions come primarily from energy production, including burning coal, oil, or natural gas.learn more. Humans generate co₂ when burning fossil fuels such as gas, petrol, oil, and coal. this adds an additional 9.1 billion tonnes of co₂ to the atmosphere each year. plants and soils take up 2.8 billion tonnes of this extra carbon, while the oceans take up 2.2 billion tonnes.
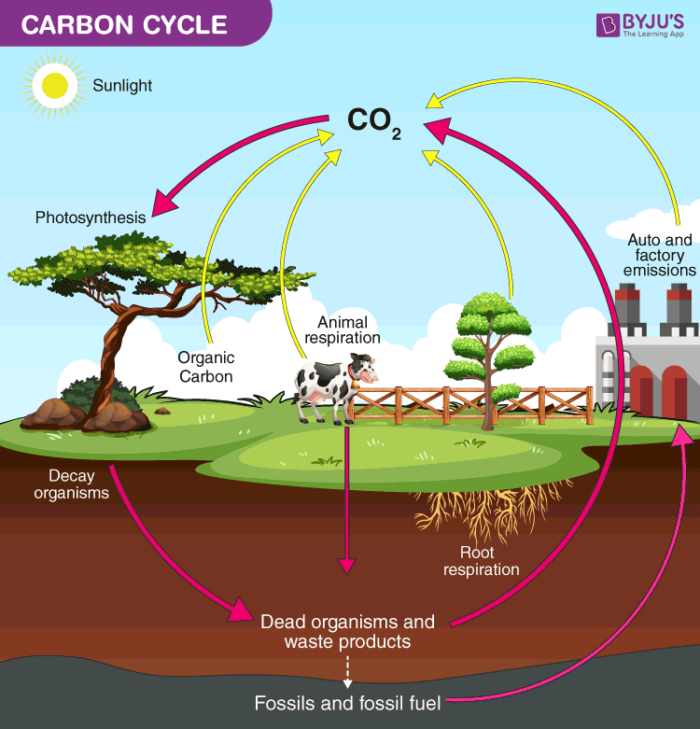
The Diagram Shows Part Of The Carbon Cycle Respiration, excretion, and decomposition release the carbon back into the atmosphere or soil, continuing the cycle. the ocean plays a critical role in carbon storage, as it holds about 50 times more carbon than the atmosphere. two way carbon exchange can occur quickly between the ocean’s surface waters and the atmosphere, but carbon may be. The process of photosynthesis involves the absorption of co 2 by plants to produce carbohydrates. the equation is as follows: co 2 h 2 o energy → (ch 2 o) n o 2. carbon compounds are passed along the food chain from the producers to consumers. the majority of the carbon exists in the body in the form of carbon dioxide through respiration. Release from rocks and fossil fuels: geological processes and human activities release carbon from rocks and fossil fuels. weathering of rocks, volcanic activity, and burning fossil fuels release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. carbon in the oceans: oceans absorb a significant amount of co 2 from the atmosphere. marine organisms use. However, the slow carbon cycle also contains a slightly faster component: the ocean. at the surface, where air meets water, carbon dioxide gas dissolves in and ventilates out of the ocean in a steady exchange with the atmosphere. once in the ocean, carbon dioxide gas reacts with water molecules to release hydrogen, making the ocean more acidic.

Comments are closed.