How To Calculate Surface Area Gcse Maths Steps Examples 6 × 4 = 24. right side. 24. 2 add the areas together. the sum of the areas is: 40 40 60 60 24 24 = 24840 40 60 60 24 24 = 248. 3 write the answer, including the units. the measurements are in cmcm so the surface area will be measured in cm 2cm2. total surface area = 248cm 2= 248cm2. Example 3: calculate the surface area in terms of pi. a chip shop sells mushy peas in a conical pot. the lid has a radius of 7cm , and the pot has a slant height of 10cm . calculate the outside surface area of the closed pot, including the lid. write your answer in terms of \pi .

Surface Area A Maths Dictionary For Kids Quick Reference By Jenny Eather We then need to find the area of the base of the cylinder: area of a circle = πr2 = π × 72 = 49πarea of a circle = πr2 = π ×72 = 49π. the area of the top of the cylinder is the same as the area of the base so, total surface area: 140π 49π 49π = 238π = 747.699905…140π 49π 49π = 238π = 747.699905…. Surface area of any pyramid = area of base area of each of the lateral faces. if the pyramid is a regular pyramid, we can use the formula for the surface area of a regular pyramid. surface area of regular pyramid = area of base 1 2 ps. where p is the perimeter of the base and s is the slant height. Add together: sum the areas of the circles and the rectangle to find the total surface area. by following these steps, one can systematically compute the surface area, a key skill in gcse maths. troubleshooting common errors. when solving cylinder problems, students often encounter typical pitfalls:. Find the surface area of the cylinder, giving your answer to 4 4 significant figures. [3 marks] we know the formula for the surface area of a cylinder is. surface area = 2\pi r h 2\pi r^2 2πrh 2πr2. from the diagram we can see: – the radius, r, = 12\div 2 = 6 12 ÷ 2 = 6 mm. – the height of the cylinder is 25 25 mm.
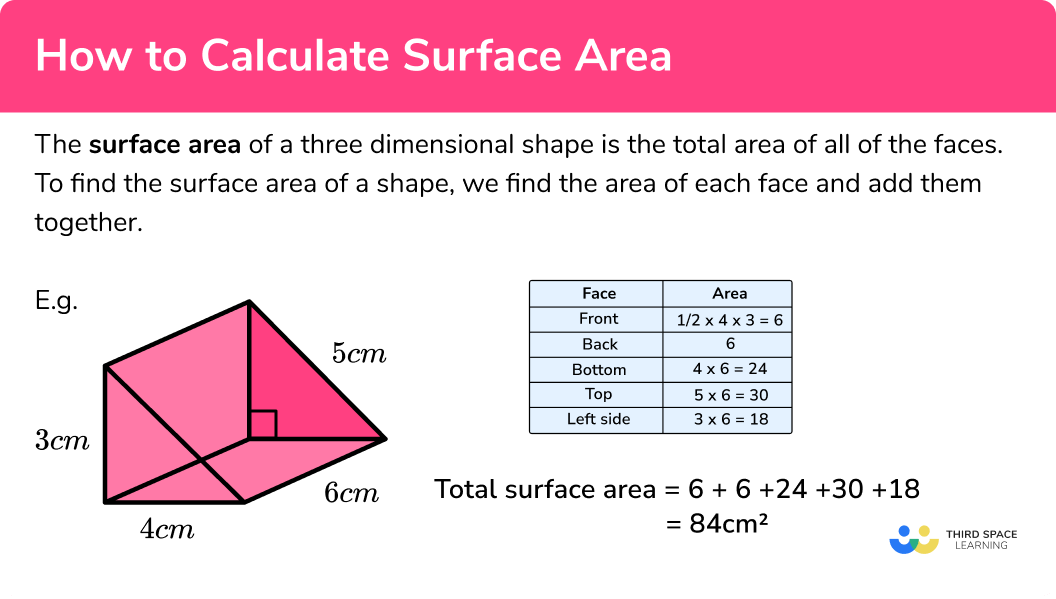
How To Calculate Surface Area Gcse Maths Steps Examples Add together: sum the areas of the circles and the rectangle to find the total surface area. by following these steps, one can systematically compute the surface area, a key skill in gcse maths. troubleshooting common errors. when solving cylinder problems, students often encounter typical pitfalls:. Find the surface area of the cylinder, giving your answer to 4 4 significant figures. [3 marks] we know the formula for the surface area of a cylinder is. surface area = 2\pi r h 2\pi r^2 2πrh 2πr2. from the diagram we can see: – the radius, r, = 12\div 2 = 6 12 ÷ 2 = 6 mm. – the height of the cylinder is 25 25 mm. Surface area of cylinders. examples, solutions, and videos to help gcse maths students learn about how to find the surface area of cylinders. the following diagram gives the surface area formula for a cylinder. scroll down the page for more examples and solutions. The volume of the cuboid is 12 cm 3. the surface area of a 3d shape is the total area of all the faces. a cube has six faces which are all squares. the area of one face is: \ (5 \times 5 = 25.

How To Calculate Surface Area Gcse Maths Steps And Examplesођ Surface area of cylinders. examples, solutions, and videos to help gcse maths students learn about how to find the surface area of cylinders. the following diagram gives the surface area formula for a cylinder. scroll down the page for more examples and solutions. The volume of the cuboid is 12 cm 3. the surface area of a 3d shape is the total area of all the faces. a cube has six faces which are all squares. the area of one face is: \ (5 \times 5 = 25.

Comments are closed.