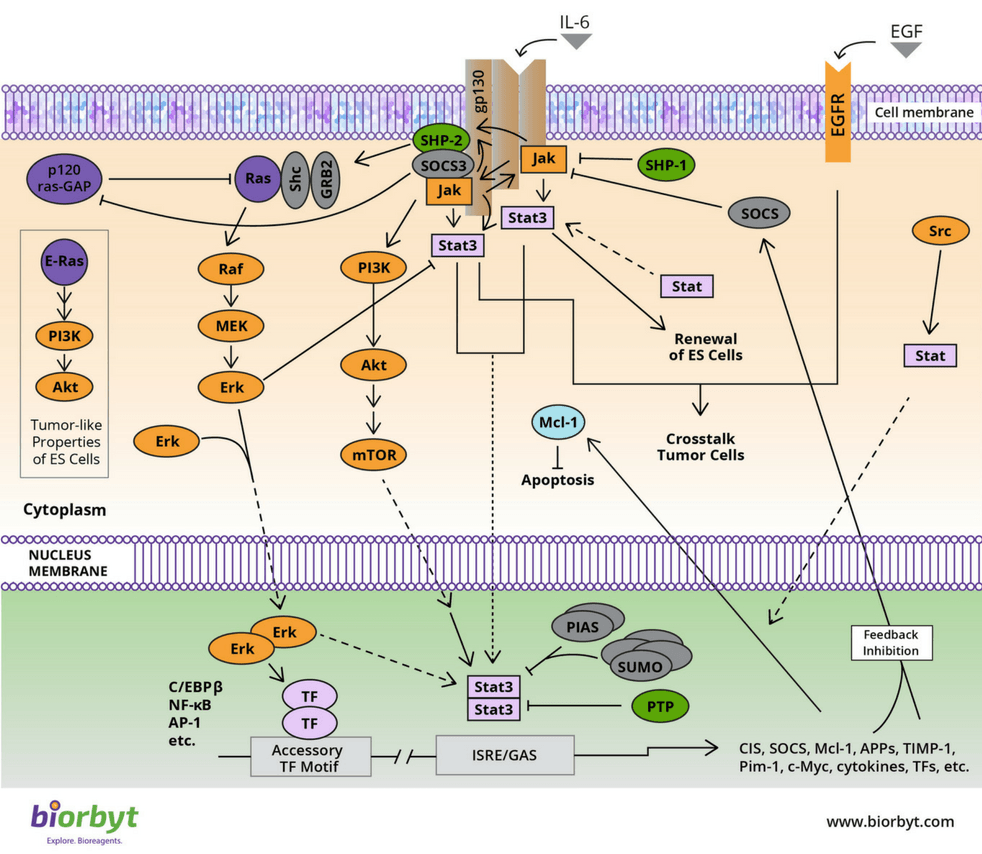
Jak Stat Signaling Pathway Biorbyt Jak stat signaling is integral to homeostatic and developmental processes such as hematopoiesis, immune development, stem cell maintenance, organismal growth and mammary gland development. the pathway is activated upon binding of an extracellular ligand, usually comprising interferons or growth factors. this results in multimerization of the. The jak stat pathway is an important cascade of signal transduction for multiple growth factors and cytokines, which regulates gene expression and cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation (reddy et al., 2019; xin et al., 2020; awasthi et al., 2021). the jak stat pathway has three components: cellular receptors, jak protein, and stat.
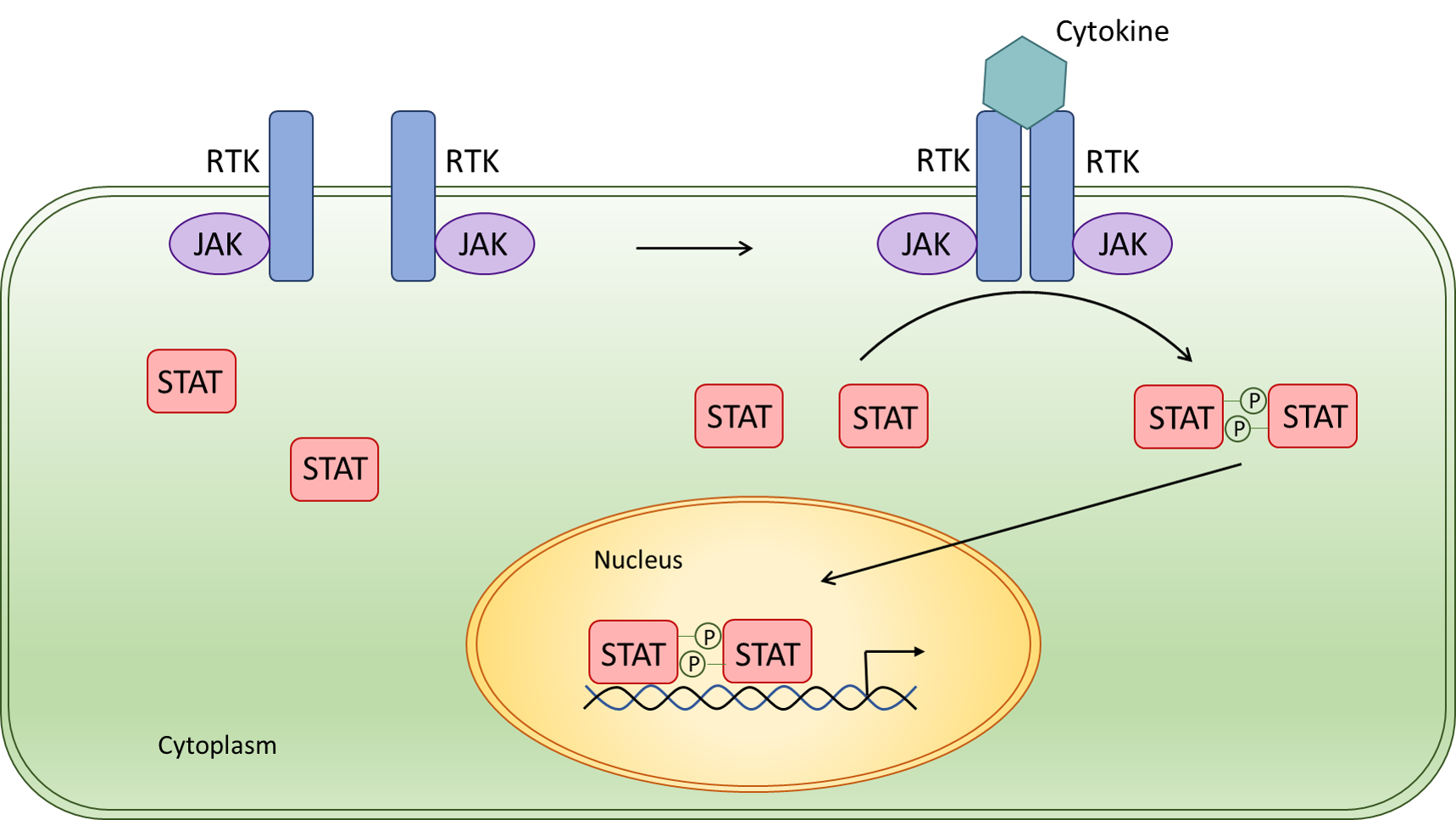
Jak Stat Signal Pathway Creative Biomart The jak stat signaling pathway is evolutionarily conserved. it is composed of ligand receptor complexes, jaks, and stats. there are 4 members in the jak family: jak1, jak2, jak3, and tyk2. The story of the janus kinase signal transducer and activator of transcription (jak stat) pathway can be traced back to the year 1957 when alick isaacs and jean lindenmann conducted investigations. Discovery of the jak stat signaling pathway. the jak stat signaling pathway was first discovered when studying how ifns lead to the activation of a transcription factor. 11 in 1990, the transcriptional activator interferon stimulated gene factor 3 (isgf3), a transcription factor that responds to ifn α, was discovered to be composed of multiple interacting polypeptide chains (48, 84, 91, and. The jak stat signaling pathway is a chain of interactions between proteins in a cell, and is involved in processes such as immunity, cell division, cell death, and tumour formation. the pathway communicates information from chemical signals outside of a cell to the cell nucleus, resulting in the activation of genes through the process of.

Comments are closed.