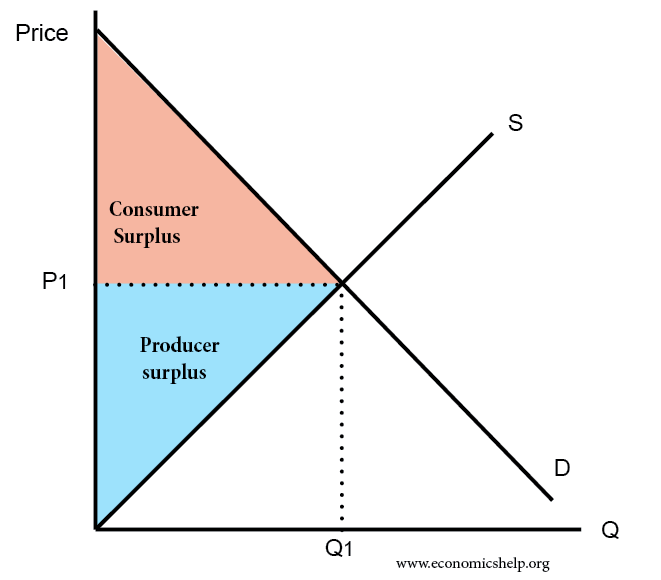
Consumer Surplus And Producer Surplus Economics Help In the previous example, the total consumer surplus was $3, and the total producer surplus $4, respectively. the total surplus, therefore, will be $7 ($3 $4). below is the formula: total surplus = consumer surplus producer surplus. in the above example, the total surplus does not depict the equilibrium. there is a deadweight to shed off. Learn the definitions, diagrams and examples of consumer surplus and producer surplus in economics. find out how elasticity, monopolies, price discrimination and free trade affect these concepts.

Consumer And Producer Surplus Edexcel Economics Revision Discover how to measure the welfare of consumers and producers in a market, and how it is affected by various policies and events. Learn how to calculate and illustrate consumer surplus, producer surplus, and social surplus using demand and supply curves. see how efficiency and allocative efficiency are related to surplus concepts. From figure 1 the following formula can be derived for consumer and producer surplus: consumer surplus = (qe x (p2 – pe)) ÷ 2. producer surplus = (qe x (pe – p1)) ÷ 2. where: qe is the equilibrium price. pe is the equilibrium price. p2 is the y intercept of the demand curve. p1 is the y intercept of the supply curve. Producer surplus is an economic measure of the difference between the amount a producer of a good receives and the minimum amount the producer is willing to accept for the good. the difference, or.

Economics 101 9 Consumer And Producer Surplus Piigsty From figure 1 the following formula can be derived for consumer and producer surplus: consumer surplus = (qe x (p2 – pe)) ÷ 2. producer surplus = (qe x (pe – p1)) ÷ 2. where: qe is the equilibrium price. pe is the equilibrium price. p2 is the y intercept of the demand curve. p1 is the y intercept of the supply curve. Producer surplus is an economic measure of the difference between the amount a producer of a good receives and the minimum amount the producer is willing to accept for the good. the difference, or. How price controls reallocate surplus. price ceilings and price floors. taxation and dead weight loss. example breaking down tax incidence. percentage tax on hamburgers. taxes and perfectly inelastic demand. taxes and perfectly elastic demand. economic efficiency. The bottom line. consumer surplus is the economic benefit a consumer receives when they buy a product for less than they were willing to pay for it. producer surplus is the benefit a producer.
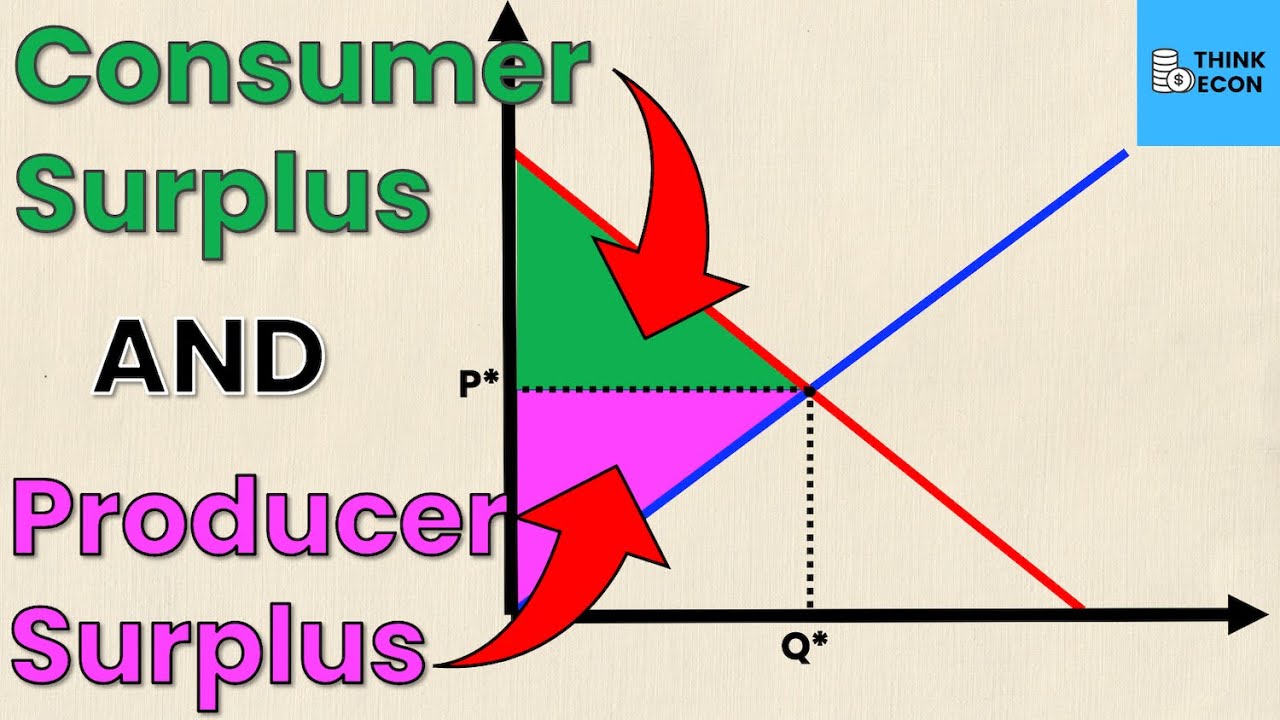
How To Calculate Producer Surplus And Consumer Surplus From Supply And How price controls reallocate surplus. price ceilings and price floors. taxation and dead weight loss. example breaking down tax incidence. percentage tax on hamburgers. taxes and perfectly inelastic demand. taxes and perfectly elastic demand. economic efficiency. The bottom line. consumer surplus is the economic benefit a consumer receives when they buy a product for less than they were willing to pay for it. producer surplus is the benefit a producer.

Consumer And Producer Surplus Youtube

Comments are closed.