
Semi Analytic Resampling In Generalized Linear Models Youtube In section 2, we describe ss in generalized linear models (glms) that we will focus on, and in section 3, we derive the proposed algorithm using the replica method and vamp. in section 4 , we analyze the proposed algorithm in a large system limit under the assumption that the set of features is characterized by rotation invariant matrix ensembles. J. stat. mech. (2020) 093402. semi analytic approximate stability selection for correlated data in generalized linear models. the advantage of this formula is that for integersn r, the negative power of the partition function (z(β)(c,γ))−ris eliminated by an integral with respect tonrepli cated variables.
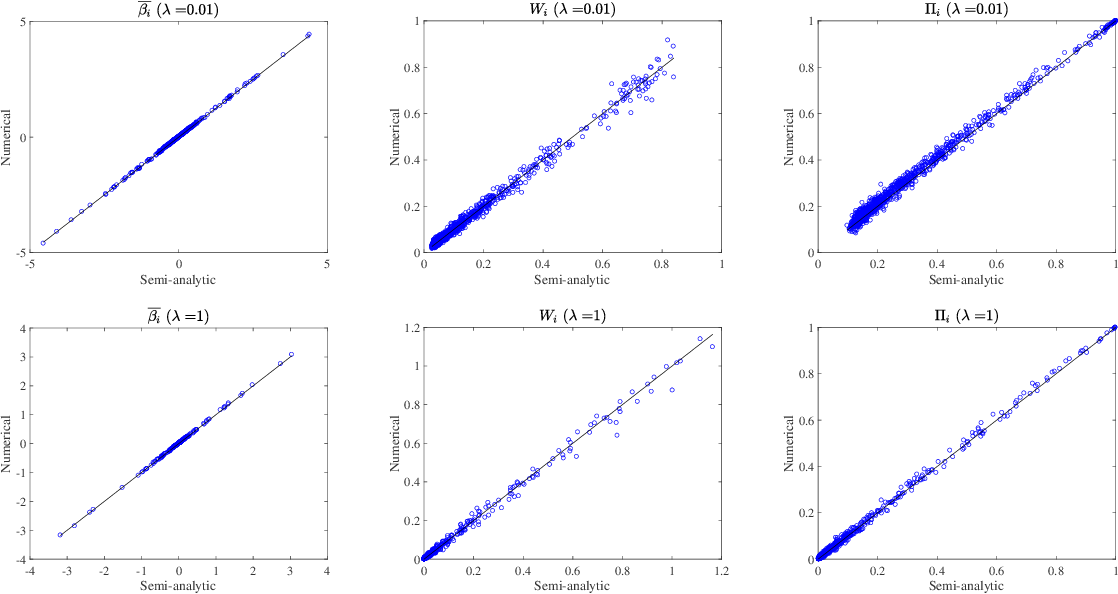
Figure 1 From Semi Analytic Resampling In Lasso Semantic Scholar Selection in generalized linear models (glms) that we will focus on, and in section 3, we derive the proposed algorithm using the replica method and v amp. in section 4, we. Semi analytic approximate stability selection fo r correlated data in generalized linear models in the rest of the paper, we will omit the argument d when there is no risk of confusion to av oid. We consider the variable selection problem of generalized linear models (glms). stability selection (ss) is a promising method proposed for solving this problem. although ss provides practical variable selection criteria, it is computationally demanding because it needs to fit glms to many re sampled datasets. We consider the variable selection problem of generalized linear models (glms). stability selection (ss) is a promising method proposed for solving this problem. although ss provides practical variable selection criteria, it is computationally demanding because it needs to fit glms to many re sampled datasets. we propose a novel approximate inference algorithm that can conduct ss without the.
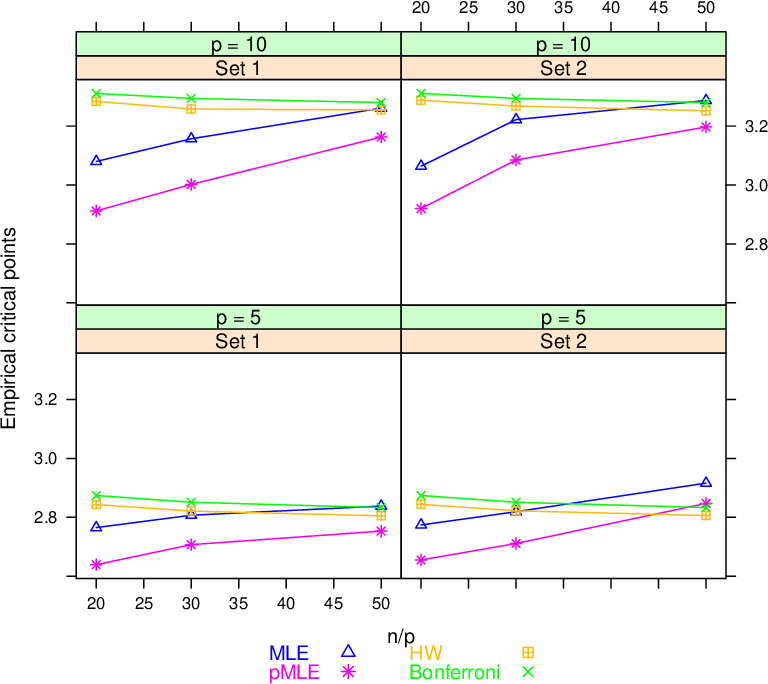
Figure 4 2 From Resampling Based Multiple Comparisons For Generalized We consider the variable selection problem of generalized linear models (glms). stability selection (ss) is a promising method proposed for solving this problem. although ss provides practical variable selection criteria, it is computationally demanding because it needs to fit glms to many re sampled datasets. We consider the variable selection problem of generalized linear models (glms). stability selection (ss) is a promising method proposed for solving this problem. although ss provides practical variable selection criteria, it is computationally demanding because it needs to fit glms to many re sampled datasets. we propose a novel approximate inference algorithm that can conduct ss without the. A novel approximate inference algorithm is proposed that can conduct stability selection without the repeated fitting of glms and exhibits fast convergence and high approximation accuracy for both synthetic and real world data. we consider the variable selection problem of generalized linear models (glms). stability selection (ss) is a promising method proposed for solving this problem. The linear mixed effects model with normal errors is a popular model for the analysis of repeated measures and longitudinal data. the generalized linear model is useful for data that have non normal errors but where the errors are uncorrelated.
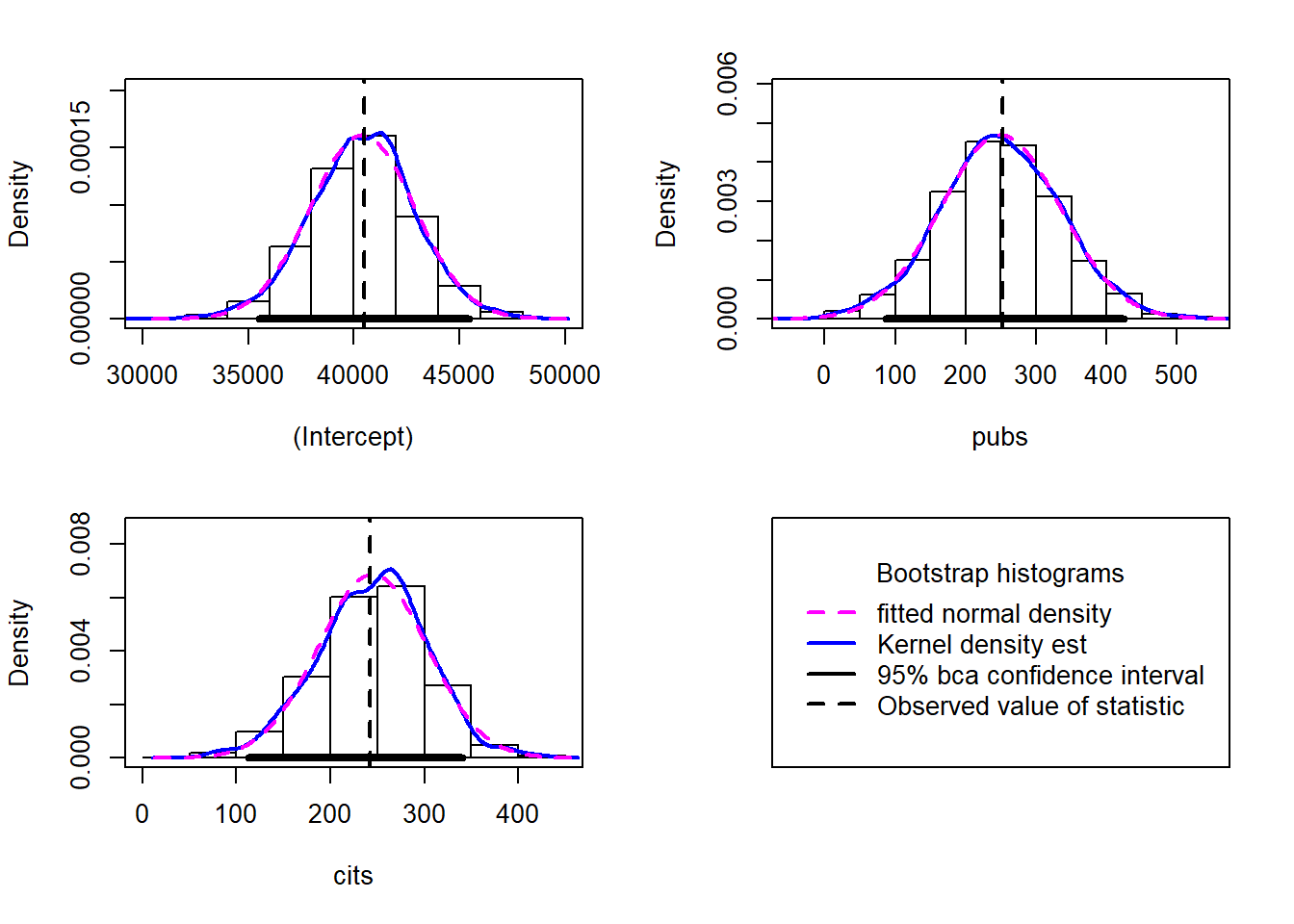
Chapter 12 Resampling And Robust Methods For Linear Models Linear A novel approximate inference algorithm is proposed that can conduct stability selection without the repeated fitting of glms and exhibits fast convergence and high approximation accuracy for both synthetic and real world data. we consider the variable selection problem of generalized linear models (glms). stability selection (ss) is a promising method proposed for solving this problem. The linear mixed effects model with normal errors is a popular model for the analysis of repeated measures and longitudinal data. the generalized linear model is useful for data that have non normal errors but where the errors are uncorrelated.

Semi Analytic Approximate Stability Selection For Correlated Data In

Comments are closed.