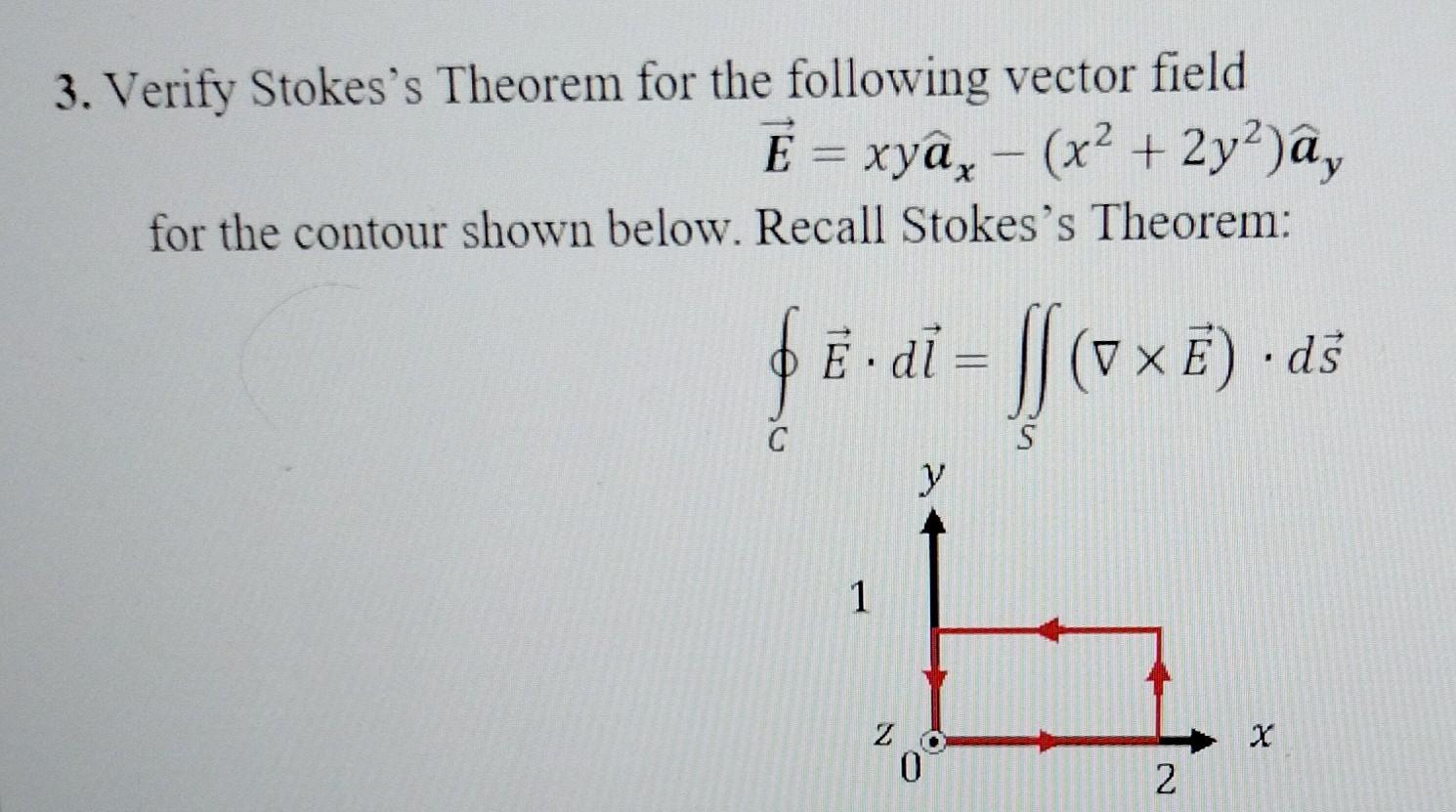
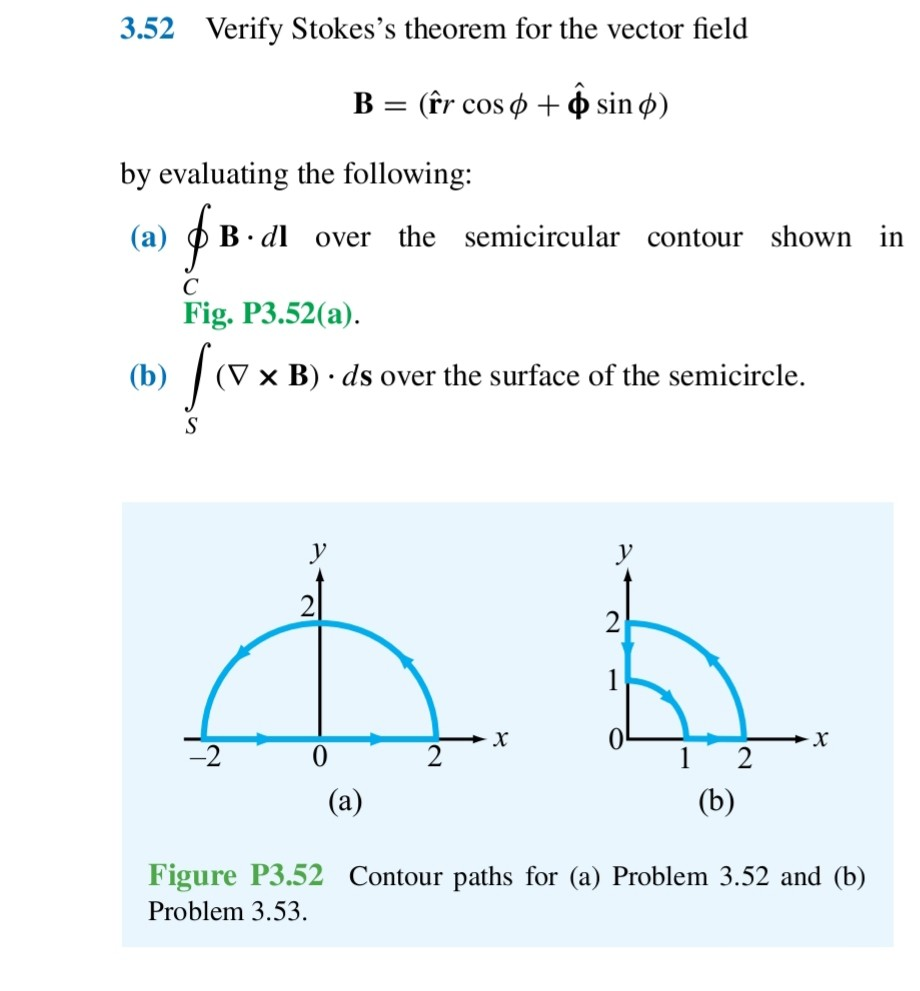
Solved 3 Verify Stokes S Theorem For The Following Vector Chegg Verify stokes's theorem for the following vector field e = x y a x − (x 2 2 y 2) a y for the contour shown below. recall stokes's theorem: ∮ c e ⋅ d l = ∬ s ( ∇ × e ) ⋅ d s not the question you’re looking for?. Engineering. electrical engineering. electrical engineering questions and answers. 3.52 verify stokes's theorem for the vector field b= (r^rcosϕ ϕ^sinϕ) by evaluating the following: (a) ∮cb⋅dl over the semicircular contour shown in fig. p3.52 (a). (b) ∫s (∇×b)⋅ds over the surface of the semicircle.

Solved 3 Verify Stokes S Theorem For The Following Vector Chegg Verify stokes's theorem for the following vector field vec ( g ) = 3 c o s ( φ ) w i d e h a t ( a ) ρ s i n ( φ ) w i d e h a t ( a ) φ for the contour shown below. Test stokes’ theorem for the function v = (xy)xˆ (2yz)yˆ (3zx)ˆz, using the triangular shaded area of fig. 1.34. solution the aim here is to verify stokes’s theorem, which states that s (∇×v)·ds = bdy s v ·dl, for the given triangular area s. start by evaluating the surface integral on the left, noting that. Stokes’ theorem. let s be a piecewise smooth oriented surface with a boundary that is a simple closed curve c with positive orientation (figure 6.79).if f is a vector field with component functions that have continuous partial derivatives on an open region containing s, then. 1. stoke's theorem states that for a oriented, smooth surface Σ Σ bounded simple, closed curve c c with positive orientation that. ∬Σ ∇ × f ⋅ dΣ =∫c f ⋅ dr ∬ Σ ∇ × f ⋅ d Σ = ∫ c f ⋅ d r. for a vector field f f, where ∇ × f ∇ × f denotes the curl of f f. now the surface in question is the positive hemisphere of.
Solved 3 52 Verify Stokes S Theorem For The Vector Field F Stokes’ theorem. let s be a piecewise smooth oriented surface with a boundary that is a simple closed curve c with positive orientation (figure 6.79).if f is a vector field with component functions that have continuous partial derivatives on an open region containing s, then. 1. stoke's theorem states that for a oriented, smooth surface Σ Σ bounded simple, closed curve c c with positive orientation that. ∬Σ ∇ × f ⋅ dΣ =∫c f ⋅ dr ∬ Σ ∇ × f ⋅ d Σ = ∫ c f ⋅ d r. for a vector field f f, where ∇ × f ∇ × f denotes the curl of f f. now the surface in question is the positive hemisphere of. However, this is the flux form of green’s theorem, which shows us that green’s theorem is a special case of stokes’ theorem. green’s theorem can only handle surfaces in a plane, but stokes’ theorem can handle surfaces in a plane or in space. the complete proof of stokes’ theorem is beyond the scope of this text. Example 1. let c c be the closed curve illustrated below. ∫cf ⋅ ds ∫ c f ⋅ d s. using stokes' theorem. ∬scurlf ⋅ ds, ∬ s curl f ⋅ d s, where s s is a surface with boundary c c. we have freedom to choose any surface s s, as long as we orient it so that c c is a positively oriented boundary.

Solved Problem 3 Verify Stokes S Theorem For The Vector ођ However, this is the flux form of green’s theorem, which shows us that green’s theorem is a special case of stokes’ theorem. green’s theorem can only handle surfaces in a plane, but stokes’ theorem can handle surfaces in a plane or in space. the complete proof of stokes’ theorem is beyond the scope of this text. Example 1. let c c be the closed curve illustrated below. ∫cf ⋅ ds ∫ c f ⋅ d s. using stokes' theorem. ∬scurlf ⋅ ds, ∬ s curl f ⋅ d s, where s s is a surface with boundary c c. we have freedom to choose any surface s s, as long as we orient it so that c c is a positively oriented boundary.

Solved Verify Stokes S Theorem For The Following Vector ођ

Comments are closed.