
The Importance Of Suction In Pulmonary Aspiration Emergencies The importance of suction in pulmonary aspiration emergencies. pulmonary aspiration is a common medical emergency, especially in patients with endotracheal tubes or other aspiration risk factors. in fact, one study found aspiration has been reported in about 25% of intubated patients. aspiration is a life threatening medical emergency. Airway suctioning is routinely done in most care settings, including acute care, sub acute care, long term care, and home settings. suctioning is performed when the patient is unable to effectively move secretions from the respiratory tract. this may occur with excessive production of secretions or ineffective clearance, which leads to the accumulation of secretions in the upper and lower.

Portable Emergency Suction A Critical Tool In Avoiding Aspiration Initially described by mendelson in 1946, aspiration pneumonitis is damage to the lung parenchyma resulting from inhalation of sterile, acid (or bile) gastric contents. the severity of pulmonary parenchymal injury is modified by the degree of acidity, the volume of the aspirate, and the presence or absence of particulate matter in the aspirated. It’s important to note that aspiration pneumonia frequently occurs as a result of a silent aspiration and often without the patient being aware aspiration has occurred. 3 if there’s a delay in. Avoidance of major airway complications during routine and emergency care requires avoidance of hypoxaemia, preservation of a clear airway and prevention of pulmonary aspiration of gastric contents. anaesthesia has become increasingly safe over the last few decades, arguably as a result of improved monitoring and equipment. Aspiration is common, even in healthy patients. aspiration can have significant morbidity and mortality in certain circumstances. it is categorized based on the predominant material in the aspirate. if oropharyngeal secretions, orally ingested material, or partially digested gastric contents are aspirated, one would expect infectious pneumonia to develop. however, if pure gastric secretions.
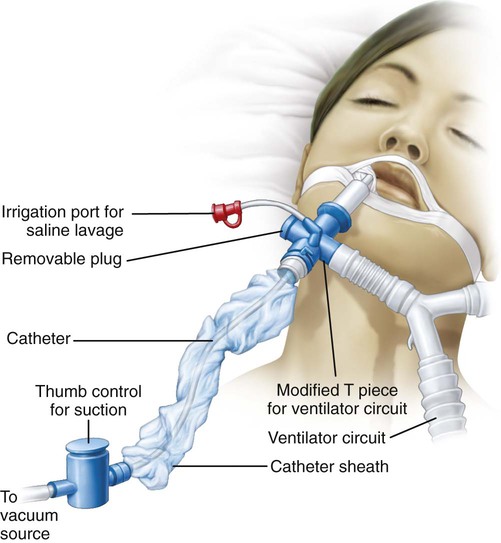
Pulmonary Therapeutic Management Nurse Key Avoidance of major airway complications during routine and emergency care requires avoidance of hypoxaemia, preservation of a clear airway and prevention of pulmonary aspiration of gastric contents. anaesthesia has become increasingly safe over the last few decades, arguably as a result of improved monitoring and equipment. Aspiration is common, even in healthy patients. aspiration can have significant morbidity and mortality in certain circumstances. it is categorized based on the predominant material in the aspirate. if oropharyngeal secretions, orally ingested material, or partially digested gastric contents are aspirated, one would expect infectious pneumonia to develop. however, if pure gastric secretions. Acute aspiration is the inhalation of foreign material into the airways beyond the vocal cords. usually occurs in patients with risk factors such as swallowing dysfunction, impaired conscious level, or substance misuse. patients with risk factors for acute aspiration should undergo a bedside clinical examination before feeding. The incidence of pulmonary aspiration in anesthesia occurs as often as 1 in every 2,000 3,000 cases. pulmonary aspiration can be a devastating complication. the incidence of pulmonary aspiration from all causes in the emergency population varies from 1 to 20% depending on the population and situation. the pre hospital incidence is as high as 39%.
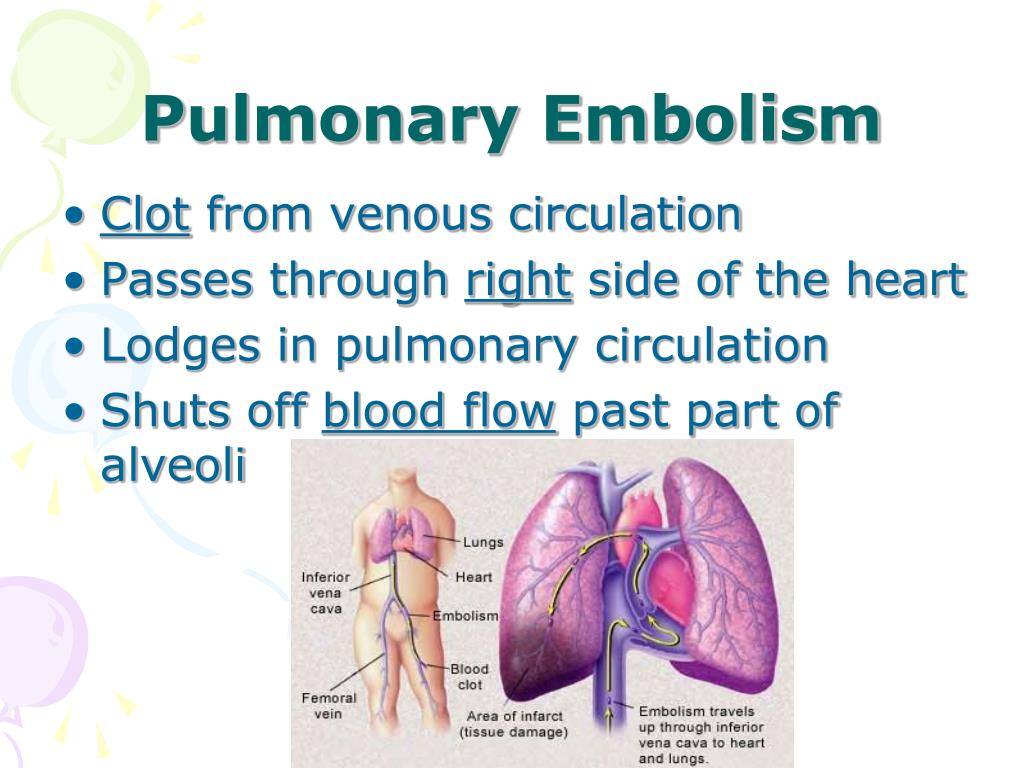
Ppt Respiratory Emergencies Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Acute aspiration is the inhalation of foreign material into the airways beyond the vocal cords. usually occurs in patients with risk factors such as swallowing dysfunction, impaired conscious level, or substance misuse. patients with risk factors for acute aspiration should undergo a bedside clinical examination before feeding. The incidence of pulmonary aspiration in anesthesia occurs as often as 1 in every 2,000 3,000 cases. pulmonary aspiration can be a devastating complication. the incidence of pulmonary aspiration from all causes in the emergency population varies from 1 to 20% depending on the population and situation. the pre hospital incidence is as high as 39%.

Comments are closed.