
Hertzsprung Russell Diagram The Location Of White Dwarfs Is Clearly Hertzsprung–russell diagram. an observational hertzsprung–russell diagram with 22,000 stars plotted from the hipparcos catalogue and 1,000 from the gliese catalogue of nearby stars. stars tend to fall only into certain regions of the diagram. the most prominent is the diagonal, going from the upper left (hot and bright) to the lower right. The group called the main sequence extends in a rough diagonal from the upper left of the diagram (hot, bright stars) to the lower right (dim and cool). large, bright, though cool, stars called giants and supergiants appear in the upper right, and the white dwarfs, dim, small, and hot, lie in the lower left.
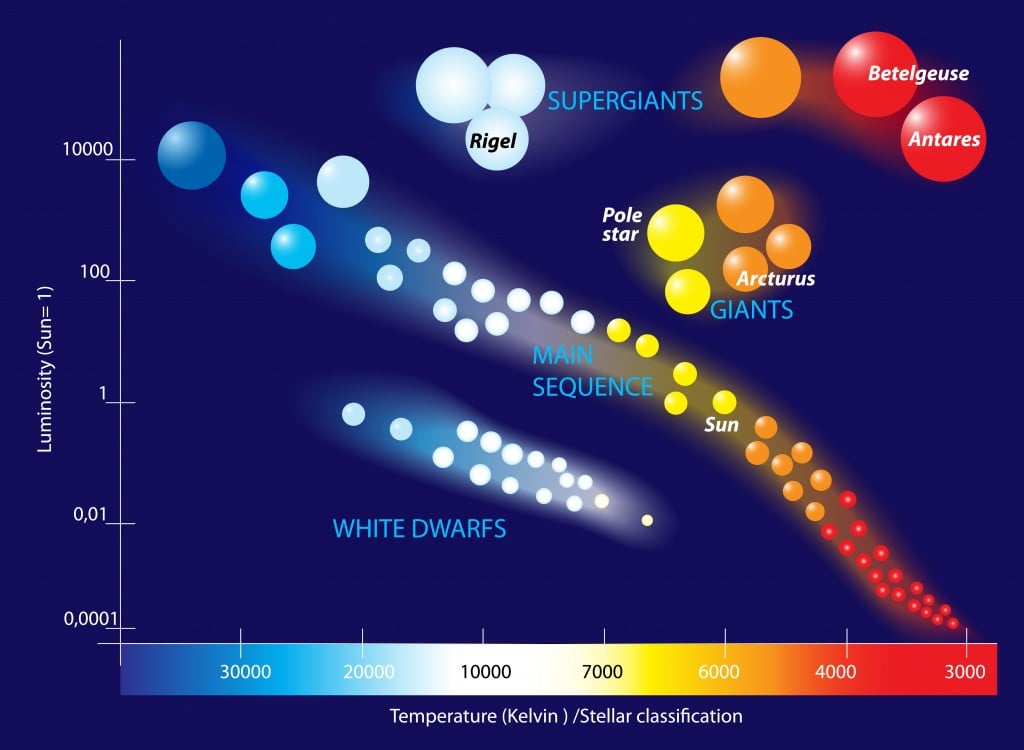
White Dwarf Definition Size Temperature And Other Facts The cool supergiants in the upper corner of the h–r diagram are as much as 10,000 times as luminous as the sun. in addition, these stars have diameters very much larger than that of the sun. as discussed above, some supergiants are so large that if the solar system could be centered in one, the star’s surface would lie beyond the orbit of. Hertzsprung russell diagram. the hertzsprung russell diagram shows the relationship between a star's temperature and its luminosity. it is also often called the h r diagram or colour magnitude diagram. it is a very useful graph because it can be used to chart the life cycle of a star. we can use it to study groups of stars in clusters or galaxies. One of the best ways to summarize all of these details about how a star or protostar changes with time is to use a hertzsprung russell (h–r) diagram. recall from the stars: a celestial census that, when looking at an h–r diagram, the temperature (the horizontal axis) is plotted increasing toward the left. as a star goes through the stages. This particular h r diagram uses only the 4907 best parallaxes measured by hipparcos, and so it excludes the many faint white dwarf stars with poorer quality parallaxes; only a handful of white dwarfs are close enough, and hence bright enough, to yield 5% accuracy parallaxes. this is an example of what we call a "selection effect".

The Formation Of White Dwarf Stars Stellar Evolution One of the best ways to summarize all of these details about how a star or protostar changes with time is to use a hertzsprung russell (h–r) diagram. recall from the stars: a celestial census that, when looking at an h–r diagram, the temperature (the horizontal axis) is plotted increasing toward the left. as a star goes through the stages. This particular h r diagram uses only the 4907 best parallaxes measured by hipparcos, and so it excludes the many faint white dwarf stars with poorer quality parallaxes; only a handful of white dwarfs are close enough, and hence bright enough, to yield 5% accuracy parallaxes. this is an example of what we call a "selection effect". Hertzsprung–russell (hr) diagram with the stars (black dots in figure 2). the white dwarfs were so varied—spanning a wide range of masses, luminosities, temperatures, and ages—that tremblay and company were able to search the hr diagram for a telltale pattern in the num ber density predicted by theory. a his togram of the number of white. Hertzsprung russell diagram. the hr diagram is the "rosetta stone" of stellar astronomy. it was created in 1910 by ejnar hertzsprung and henry norris russell. it plots a star's luminosity against its surface temperature. as simple as that sounds, it is the key to understanding stellar evolution.
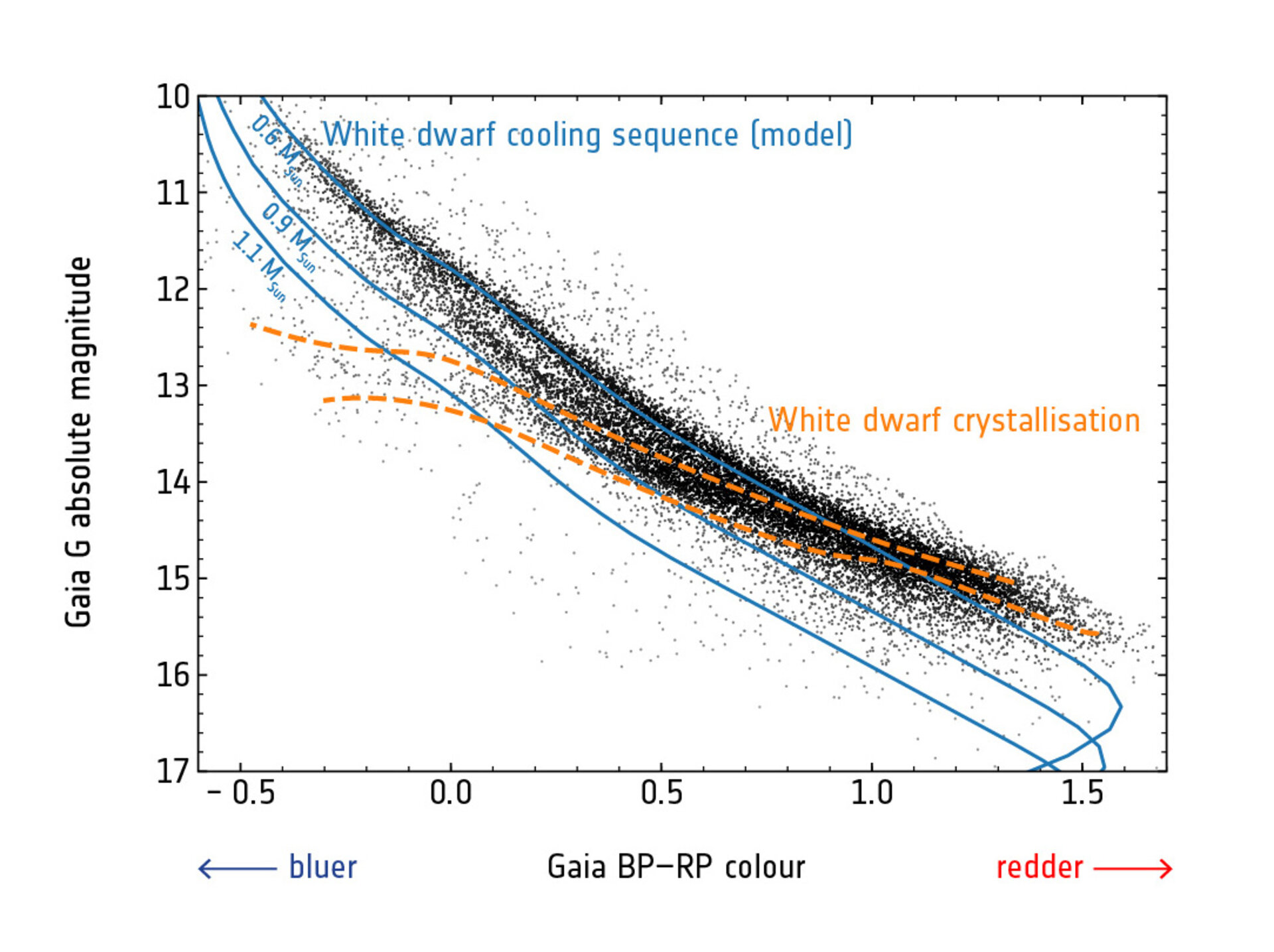
Esa White Dwarf Cooling Sequence And Crystallisation Hertzsprung–russell (hr) diagram with the stars (black dots in figure 2). the white dwarfs were so varied—spanning a wide range of masses, luminosities, temperatures, and ages—that tremblay and company were able to search the hr diagram for a telltale pattern in the num ber density predicted by theory. a his togram of the number of white. Hertzsprung russell diagram. the hr diagram is the "rosetta stone" of stellar astronomy. it was created in 1910 by ejnar hertzsprung and henry norris russell. it plots a star's luminosity against its surface temperature. as simple as that sounds, it is the key to understanding stellar evolution.

As White Dwarfs Cool They Move Toward The Lower Right In The Hвђ R

Comments are closed.