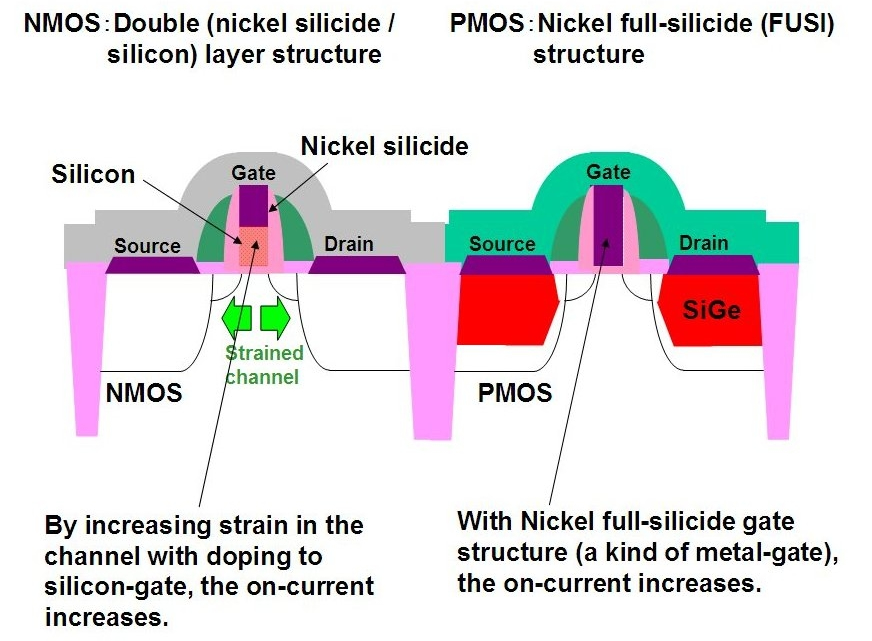
Fujitsu Laboratories Develops Low Power Cmos Technology For 32nm In this video. reason of low heat dissipation of cmos explained compared with nmos and pmos.cmos power dissipation is explained in this video. In this chapter, we explain the two types of power consumption found in a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (cmos) circuit. in general, a cmos circuit tends to dissipate power at all times—be it active or inactive. the power consumed by the circuit when it is performing computational tasks is known as dynamic power. on the contrary, the power lost due to current leakage during which.
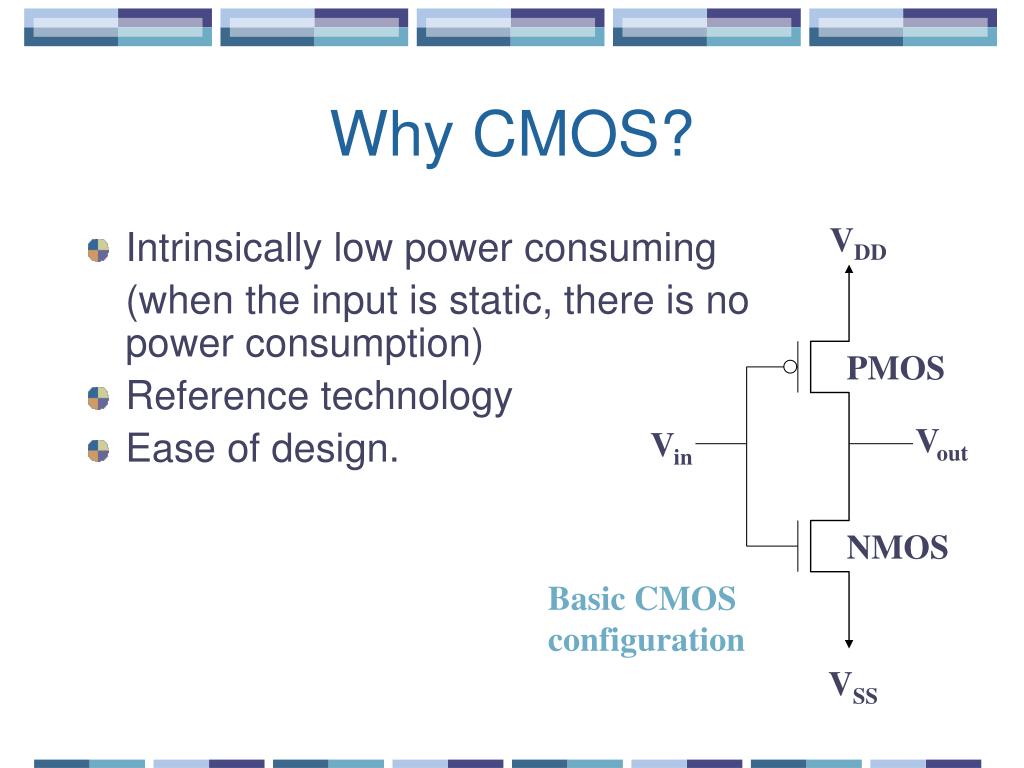
Ppt Introduction To Low Power Design Powerpoint Presentation Free This gives them a small amount of capacitance, but virtually infinite resistance. the current in or out of a cmos input held at one level is just leakage, usually 1 µa or less. the outputs actively drive both ways. the outputs are pretty much rail to rail. cmos logic consumes very little power when held in a fixed state. Reduced power dissipation in cmos circuits is a vital challenge in this cutting edge technology. it is most important when the size of transistors is scaled down to enhance transistor density over the silicon chip. power dissipation reduction is another essential goal in the designs. in a cmos circuit, overall power dissipation may be stated as. Complementary metal oxide semiconductor (cmos) power consumption is the amount of electrical power consumed by cmos circuits during operation. cmos power consumption components can be broken down into static, dynamic, short circuit, and clock power consumption. cmos power consumption affects several aspects of pcb design, including power. Conclusion. cmos power dissipation is a complex and multifaceted challenge in modern electronics design. this comprehensive guide has explored the key sources of power dissipation, including dynamic power, short circuit power, leakage power, static power, power supply noise, and capacitive coupling. by understanding the underlying principles.
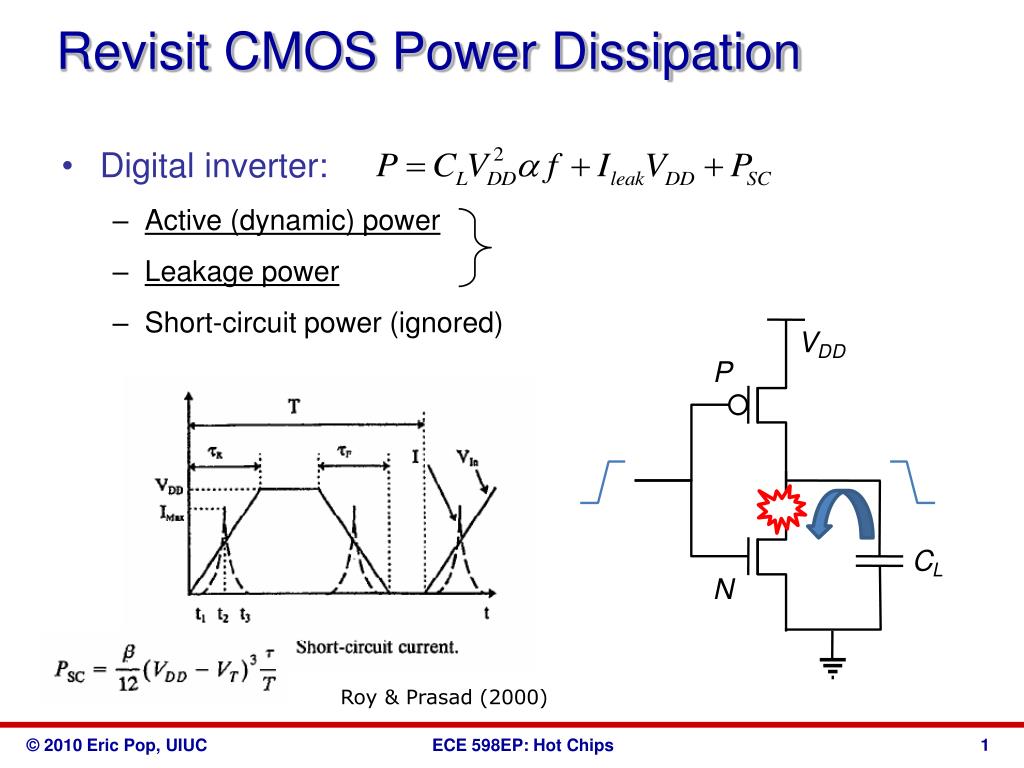
Ppt Revisit Cmos Power Dissipation Powerpoint Presentation Free Complementary metal oxide semiconductor (cmos) power consumption is the amount of electrical power consumed by cmos circuits during operation. cmos power consumption components can be broken down into static, dynamic, short circuit, and clock power consumption. cmos power consumption affects several aspects of pcb design, including power. Conclusion. cmos power dissipation is a complex and multifaceted challenge in modern electronics design. this comprehensive guide has explored the key sources of power dissipation, including dynamic power, short circuit power, leakage power, static power, power supply noise, and capacitive coupling. by understanding the underlying principles. Cmos power dissipation refers to the amount of power dissipated by complementary metal oxide semiconductor (cmos) integrated circuits (ics) during operation. cmos is widely used in modern electronic devices, such as microprocessors, memory chips, and other digital logic circuits, due to its low power consumption, high noise immunity, and. Body of the transistor is often connected to the source (no body bias) introducing a body bias modulates threshold voltage. forward body bias (fbb): increases threshold voltage. reverse body bias (rbb): reduces threshold voltage. h = h0 −. bulk cmos: effect of body bias decreases for technologies below 100nm.

Ppt Low Power Cmos Operational Amplifier Powerpoint Presentation Cmos power dissipation refers to the amount of power dissipated by complementary metal oxide semiconductor (cmos) integrated circuits (ics) during operation. cmos is widely used in modern electronic devices, such as microprocessors, memory chips, and other digital logic circuits, due to its low power consumption, high noise immunity, and. Body of the transistor is often connected to the source (no body bias) introducing a body bias modulates threshold voltage. forward body bias (fbb): increases threshold voltage. reverse body bias (rbb): reduces threshold voltage. h = h0 −. bulk cmos: effect of body bias decreases for technologies below 100nm.
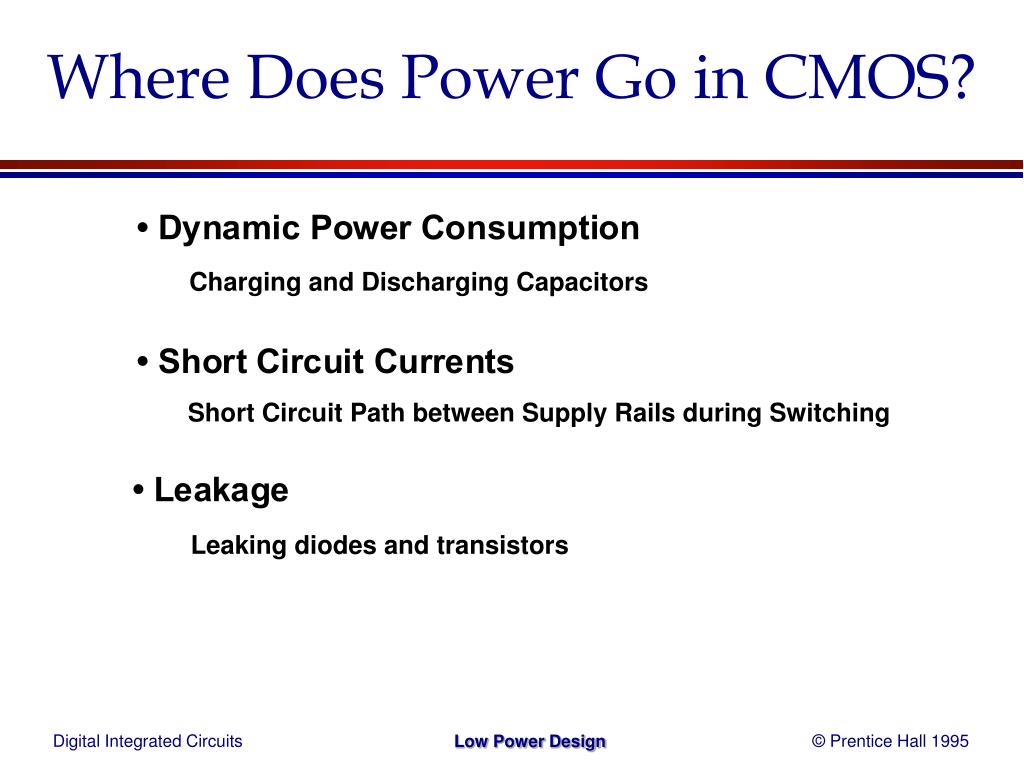
Ppt Low Power Design In Cmos Powerpoint Presentation Free Download

Comments are closed.